Bimetallic Composite Pipe
Advanced bimetallic composite pipes for enhanced durability and performance.
Bimetal wear resistant pipe adopts centrifugal casting technology in the production process of straight pipe.
This technology is to fuse and shape both metals in liquid state, realizing the purpose of real metallurgical bonding. The shear strength of the binding layer is higher than that of the metal itself, and completely realizes the mechanical complementarity between base layer and wear resistant layer.
Bimetal wear resistant pipe, including: double metal wear-resisting straight pipe and double metal wear-resisting bend, double metal wear tee, double metal wear resistance reducer adopts the pipe fittings such as vacuum suction casting composite process, its advanced technology, effectively solve the problem of the bent pipe cannot be composite, bending and other various special-shaped pipe can do the whole compound, don't change the material flow in the pipe bending trajectory, reduce resistance material conveying.
The outer wall of the centrifugal pipe is made of carbon steel, which ensures that the bimetal wear-resistant pipe has high mechanical strength and impact resistance.The inner lining wear resistance layer adopts the anti-wear alloy steel series independently developed by our company. The steel mainly adds alloy such as cr-ni-mo-cu-re and so on. Through the tempering heat treatment process, the alloy steel has strong wear resistance and corrosion resistance, high mechanical strength and impact resistance.
The whole set of process of our company is the first in China, which fills the blank of anti-corrosion and wear-resistant industrial pipeline in China and has reached the international advanced level. It has been widely used in mining, metallurgy, coal, electric power and other industries, and is an ideal wear-resistant pipeline.
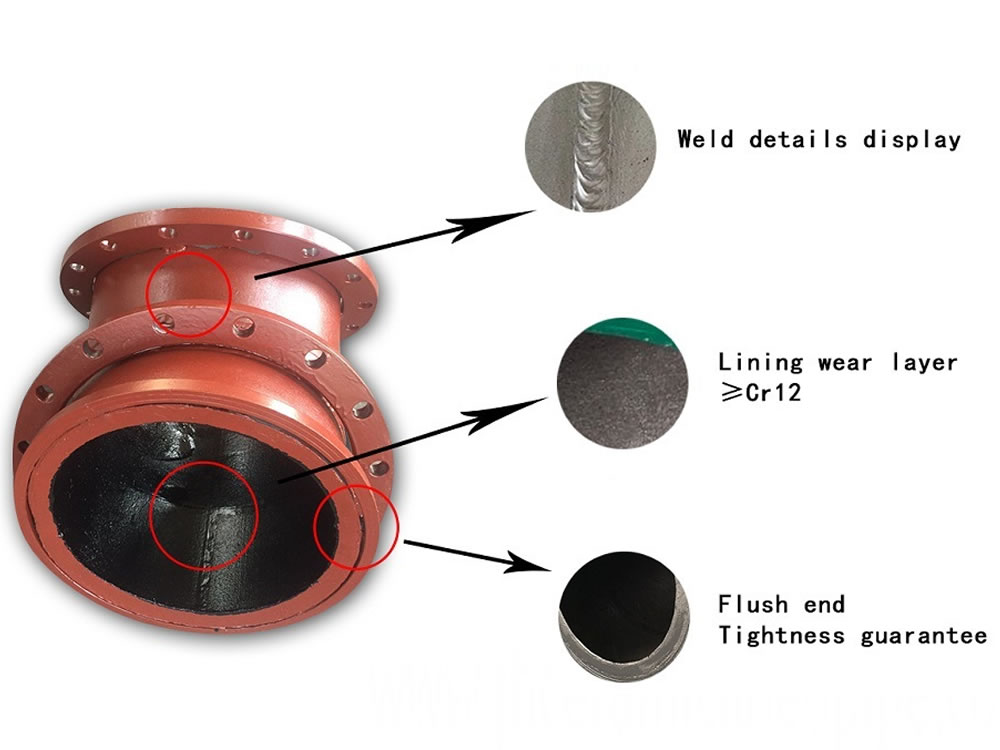
The base material is carbon steel or low alloy steel. Clad pipes comply with the most stringent requirements of strength and corrosion resistance. The carbon steel outer pipe (backing steel or base metal) complies with the static requirements of strength and durability whereas the high alloyed inside pipe provides protection against corrosion.
A bimetal or thermostatic metal is a sheet or strip of two or more composite materials having different coefficients of linear thermal expansion bonded by riveting, brazing or welding.
KmTBCr28 has the main elements of Chrome 28%, low Carbon with hardness of 430 in Brinell. KmTBCr28 is a corrosion resistant white iron suitable for low pH corrosion duties, where erosive wear is also a problem.
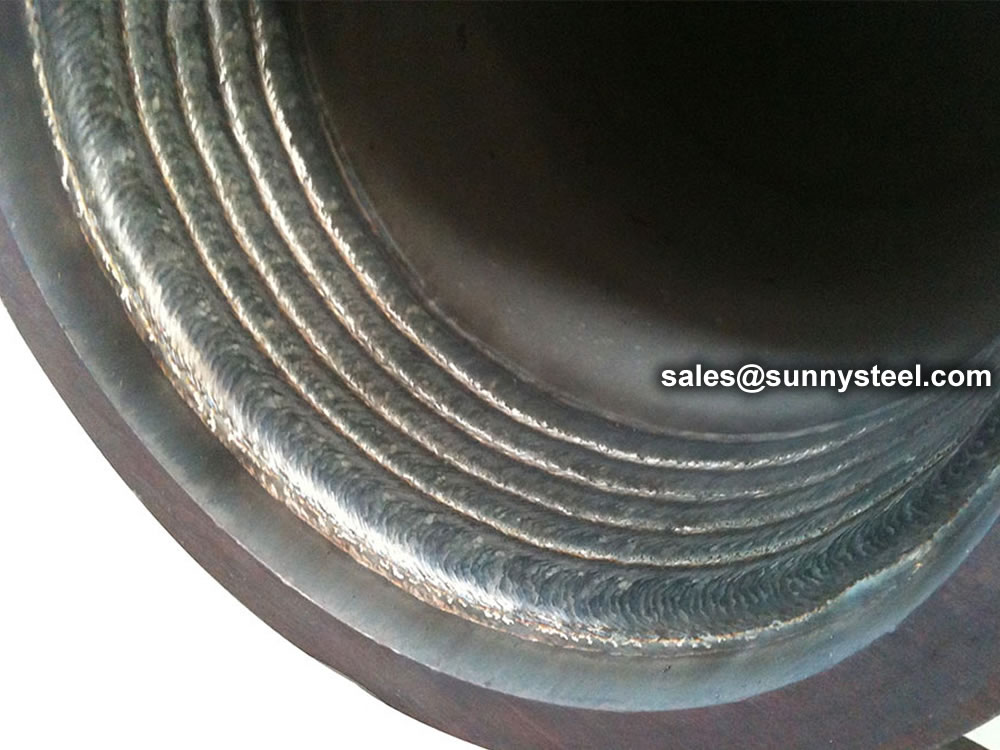

Pipe cladding is the process of covering a pipe with cladding material.
This acts as protection from problems such as wear, abrasion, corrosion, impact, etc.
Pipe cladding refers to the process of applying a protective layer or coating on the outer surface of a pipe to enhance its durability, resistance to corrosion, wear, and other environmental factors. It involves bonding a different material, typically a corrosion-resistant alloy or a high-strength metal, onto the base pipe material.
Pipe cladding is commonly used in industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, power generation, and water treatment, where pipes are exposed to harsh conditions and corrosive substances. The cladding material acts as a barrier, protecting the base pipe from corrosion, erosion, and other forms of damage.
Weld-overlay cladding: In this method, a layer of cladding material is deposited onto the base pipe through welding. Various welding processes such as manual metal arc welding (MMA), gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), or submerged arc welding (SAW) can be used depending on the cladding material and pipe size.
Explosion cladding: This technique involves using explosive energy to bond two materials together. The cladding material is generally in the form of a sheet or plate, which is explosively welded onto the base pipe.
Mechanical cladding: This method includes processes such as roll bonding and diffusion bonding. It involves mechanically bonding the cladding material onto the base pipe through pressure or heat, without the use of welding.
Pipe cladding provides several benefits, including increased resistance to corrosion, abrasion, chemicals, and high temperatures. It helps extend the lifespan of pipes, reduce maintenance costs, and improve overall performance and reliability in demanding industrial applications.
