SSIC Thermocouple Protection Tube
Designed to protect thermocouples from extreme temperatures and abrasion.
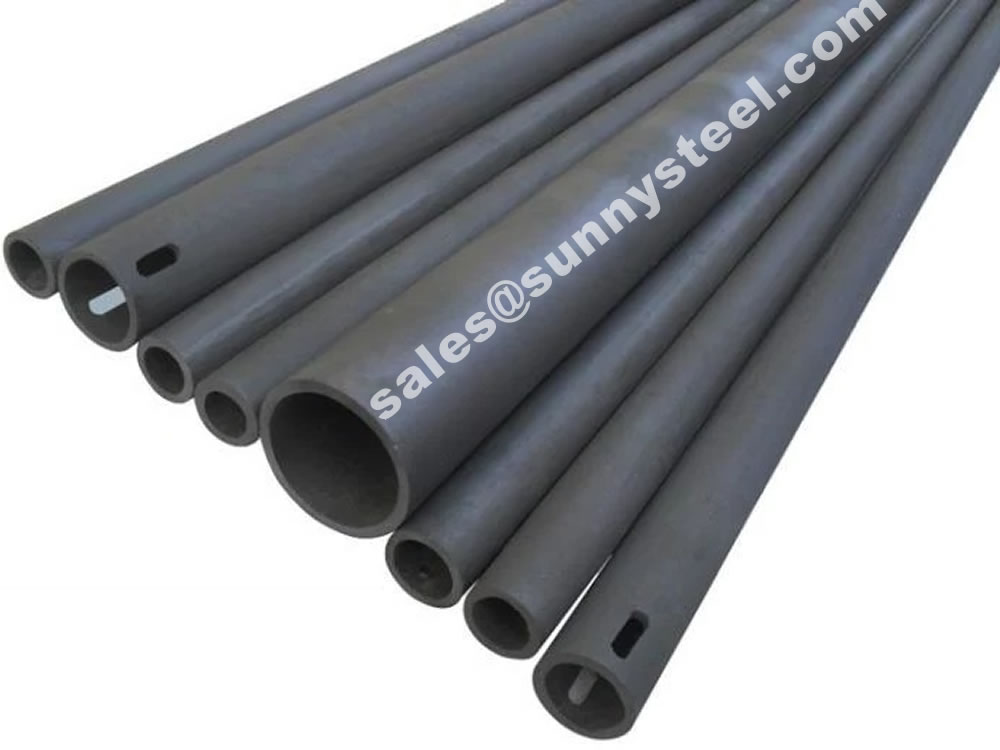

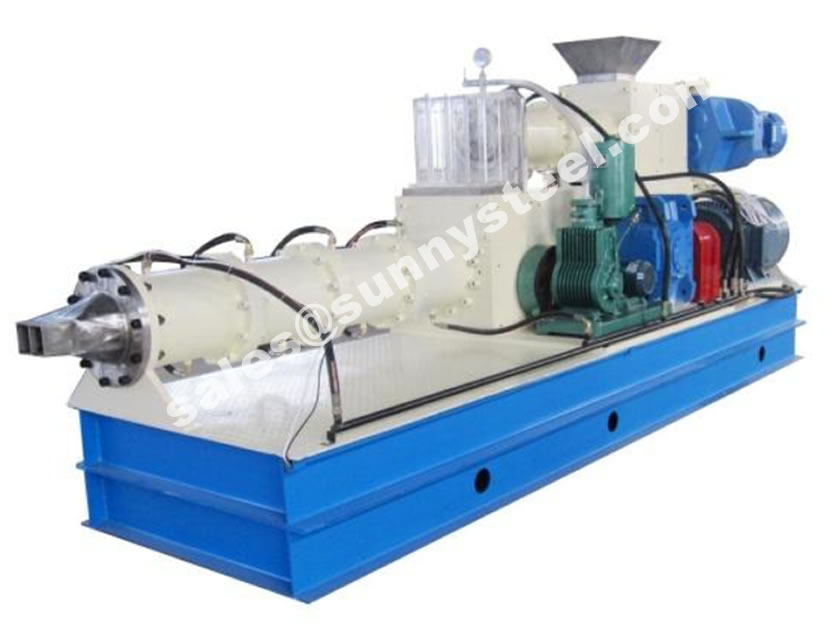
Silicon carbide Roller and Cooling Tube made by the material of siliconized silicon carbide has series of basic superiority and characteristic such as high strength, extreme hardness, wear resistance, high temperature tolerance, corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance thermal shock resistance, high thermal conductivity, low coefficient of thermal expansion, creep resistance under high temperature and so on.
Download PDFMany products can be made from it such as beams, rollers, cooling air pipes, thermal couple protection tubes, temperature-measuring tubes,sealing parts, and special shaped parts.
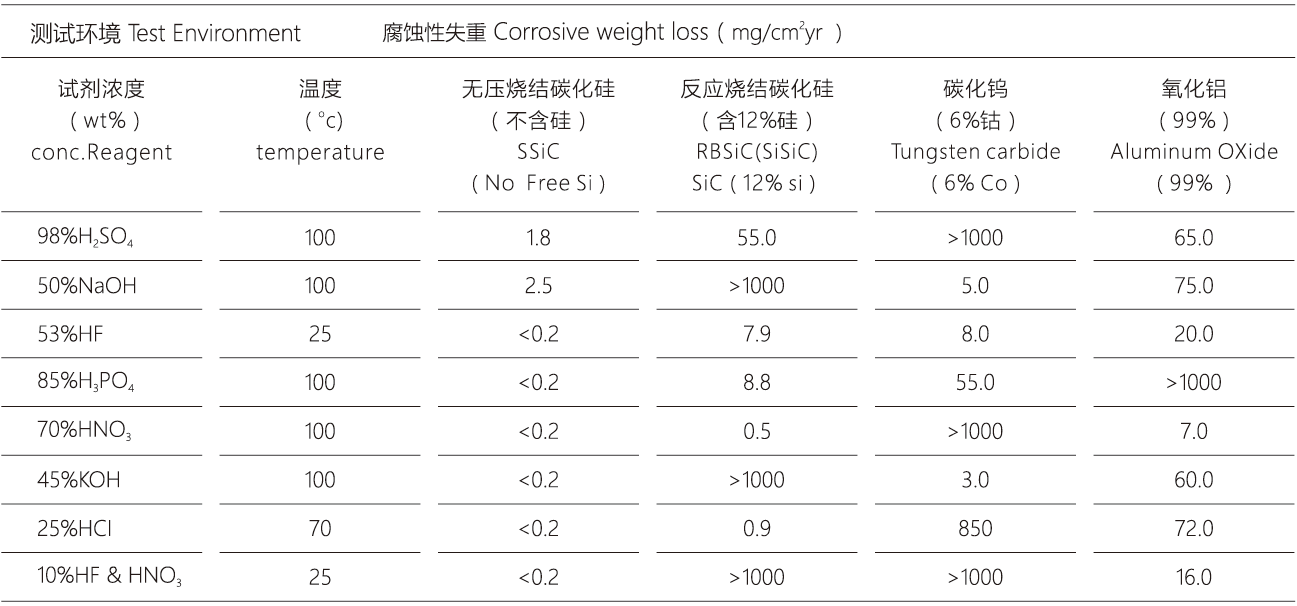
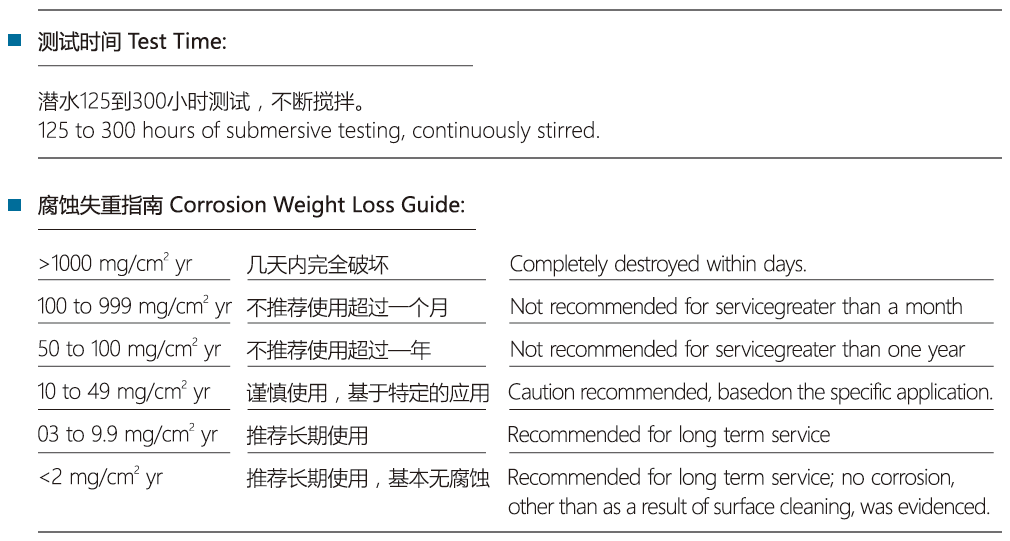
At present, there are two series silicon carbide products of pressureless sintering silicon carbide (SSIC) and reaction sintering silicon carbide (SISIC), which are widely used in mining, metallurgy, chemical industry, electric power, petroleum, furnace, machinery, steel, energy, environmental protection, building materials, semiconductor, aerospace and other fields. Compared with reaction bonded silicon carbide, pressureless sintered silicon carbide has higher purity, better mechanical properties, more prominent corrosion resistance(Resistant to strong acid and alkali corrosion, It is also the only ceramic material which can resistant to hydrofluoric acid corrosion), higher wear resistance, because of there’s no free silicon in the material. It can be used longer service life in environments which other materials not meet.
Silicon carbide (SiC) is a lightweight ceramic material with high strength properties comparable to diamond. It has excellent thermal conductivity, low thermal expansion, and is resistant to acid corrosion. Silicon carbide is an excellent ceramic material suitable for applications requiring good corrosion resistance and wear resistance.
Silicon carbide is formed in two ways, reaction bonding and sintering. Each forming method greatly affects the end microstructure.
Reaction bonded SiC is made by infiltrating compacts made of mixtures of SiC and carbon with liquid silicon. The silicon reacts with the carbon forming more SiC which bonds the initial SiC particles.
Sintered SiC is produced from pure SiC powder with non-oxide sintering aids. Conventional ceramic forming processes are used and the material is sintered in an inert atmosphere at temperatures up to 2000ºC or higher.
Both forms of silicon carbide (SiC) are highly wear resistant with good mechanical properties, including high temperature strength and thermal shock resistance. Our engineers are always available to best advise you on the strengths and weaknesses of each ceramic for your particular needs.
The crystal structure of the SiC ceramic wear-resistant pipe is similar to that of the diamond tetrahedral structure. It is a compound composed mainly of covalent bonds. Its hardness is high (Mohs 9.3), its performance is stable, and its physical properties are similar to diamond. It is also known as emery. Black silicon carbide crystal Hardness is the second-order material for diamonds. It is mainly used for making abrasives and grinding wheels, and partly for the production of silicon carbide ceramics.
| Physical Properties | Ours | International S | Local S | SISIC |
| Density(g/cc) | >3.13 | 3.07 | 3.05 | 3.02 |
| Aparant Porosity(%) | <0.1 | 0.6 | <3.0 | <0.1 |
| Bending Strength (Mpa) 20℃ 1300℃ 1600 ℃ |
390 380 430 |
380 | 320 330 350 |
250 260 - |
| Fracture Toughness (MPa.m1/2) | 4.8 | 4.6 | 3.5 | 3.8 |
| Thermal conductivity (W/mk)1250℃ |
45 | 42 | 40 | |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (10-6/℃)RT-800℃ |
3.9 | 4.6 | 4.4 | 4.5 |
| Max operating temperature* (℃) | 1700 | 1700 | 1700 | 1380 |
| Physical Properties | Ours | Local S |
| Density(g/cc) | 3.147 | 3.055 |
| Aparant Porosity(%) | 0 | 0.03 |
| Total Porosity(%) | 1.04 | 3.93 |
| Data | Company S | Ours | Difference | Increase |
| Kgf | Kgf | Kgf | % | |
| Process | Extrusion Pressing | Isostatic Pressing | ||
| Test I | 58 | 83 | 25 | 43% |
| Test II | 63 | 89 | 26 | 41% |
* O.D.:19mm * I.D.:14.5mm * Length: 800mm tube
| Data | Description |
| More Corrosion Resistant | Denser and less porosity, so more corrosion resistant. |
| More Wear-Resistant | Higher hardness, so more wear-resistant to sagging. |
| Higher Loading Capacity | Higher bending strength, so higher loading capacity. |
| More Stability | Less local defects, so more stability. |
| Longer Life | The above advantages result in a longer life. |
SSiC rollers are specialized components known for their exceptional properties, making them ideal for various applications in the ceramic industry.
The use of SSiC rollers can lead to improved product quality, increased efficiency, and cost-effectiveness due to their long service life and low maintenance requirements.
Reaction sintering silicon carbide ceramic roller is mainly used for lithium battery industry, daily porcelain, sanitary porcelain, building ceramics and magnetic materials, such as roller kiln, high temperature burning with ideal kiln, with a long service life. It has high temperature strength, thermal shock resistance, high temperature creep resistance, strong resistance, good wear resistance.
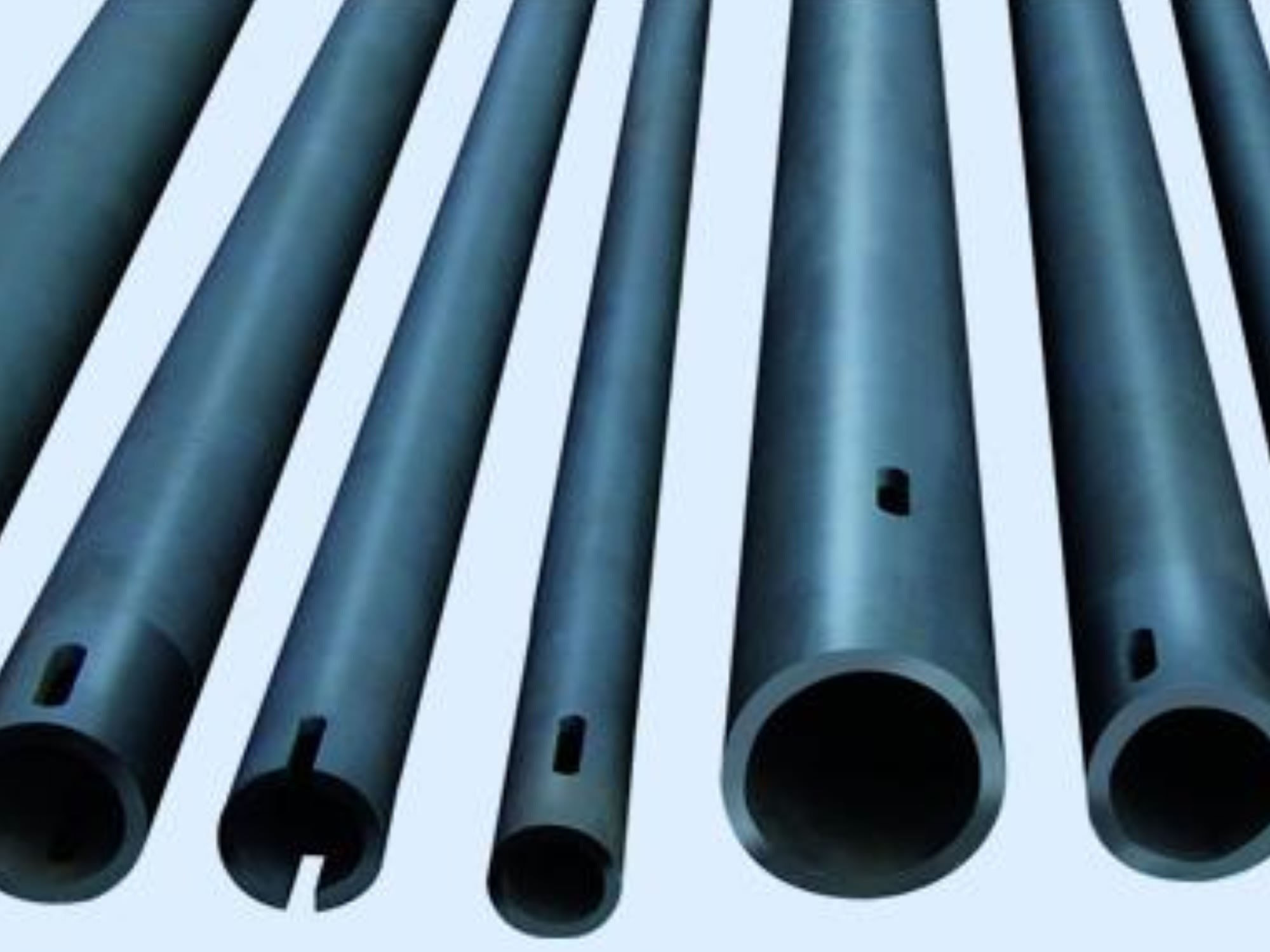
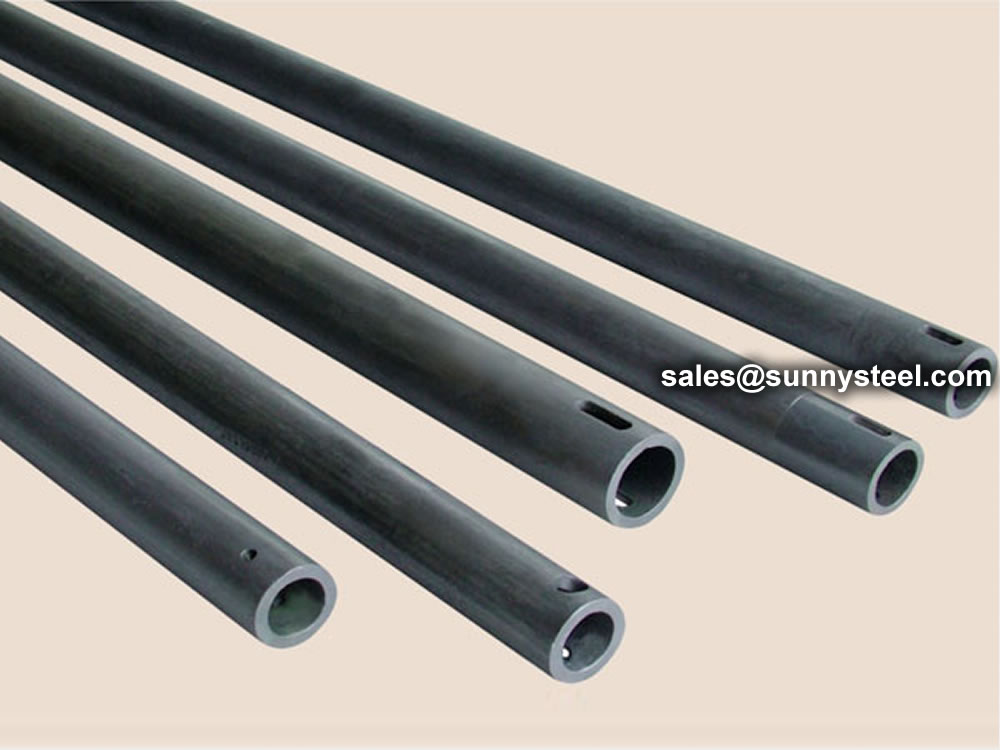
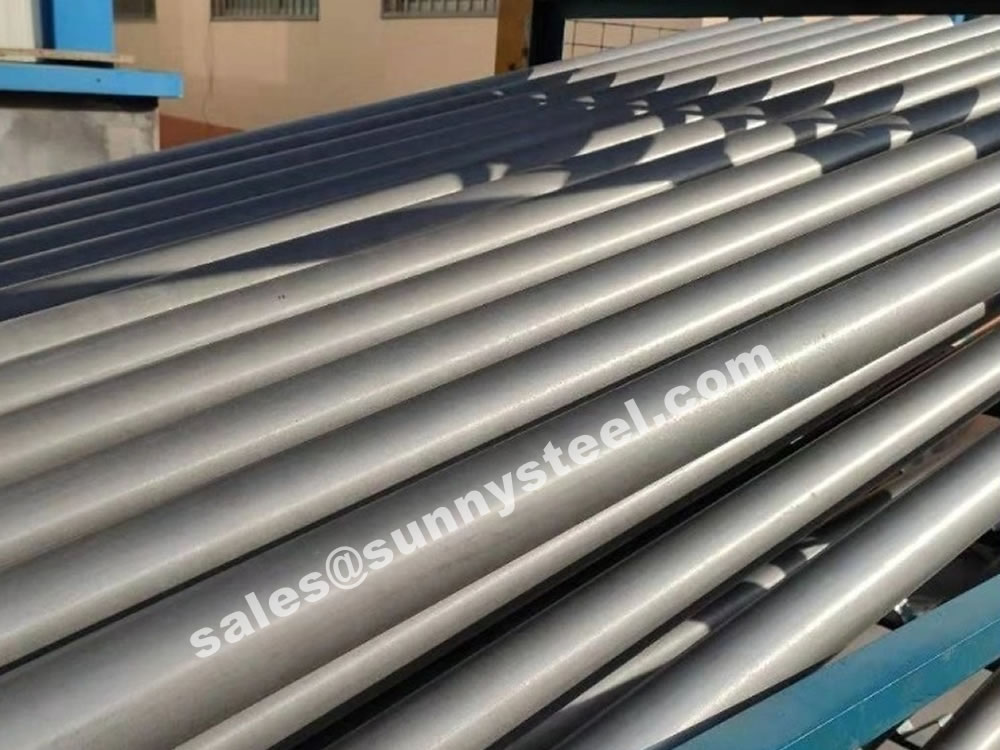
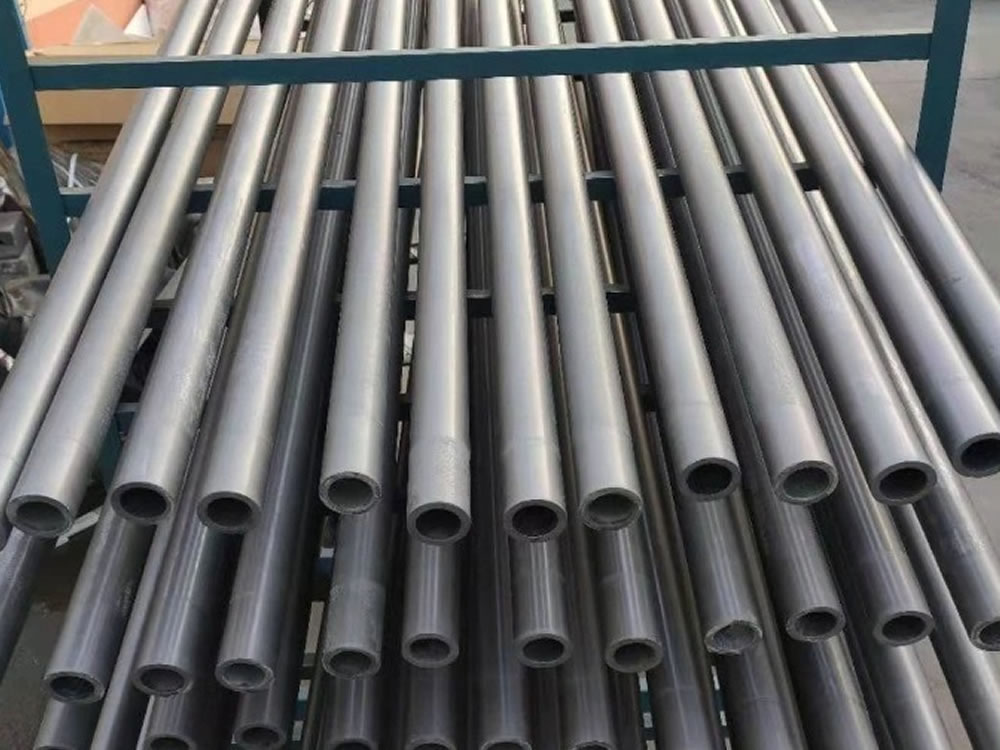











Silicon carbide was originally produced by a high-temperature electrochemical reaction of sand and carbon. Silicon carbide is an excellent abrasive and was made into grinding wheels and other abrasive products. Today the material has been developed into a high quality technical ceramic with very good mechanical properties. It is used in abrasives, refractories, ceramics and a wide range of high performance applications. Silicon carbide can also be made into an electrical conductor and has applications in resistance heating, flame igniters and electronic components.
Silicon carbide heat exchanger blocks are manufactured by direct isostatic pressing and pressureless sintering.
The heat exchange between the two media is achieved through the hole walls of the vertical and horizontal holes. The Silicon Carbide Heat Exchange Block is an innovative and high-performance solution designed for industries that require efficient heat transfer and temperature control.
The hole size can be designed according to the design requirements, the minimum hole size can reach 6mm, and the minimum hole wall thickness can reach 2.5mm.
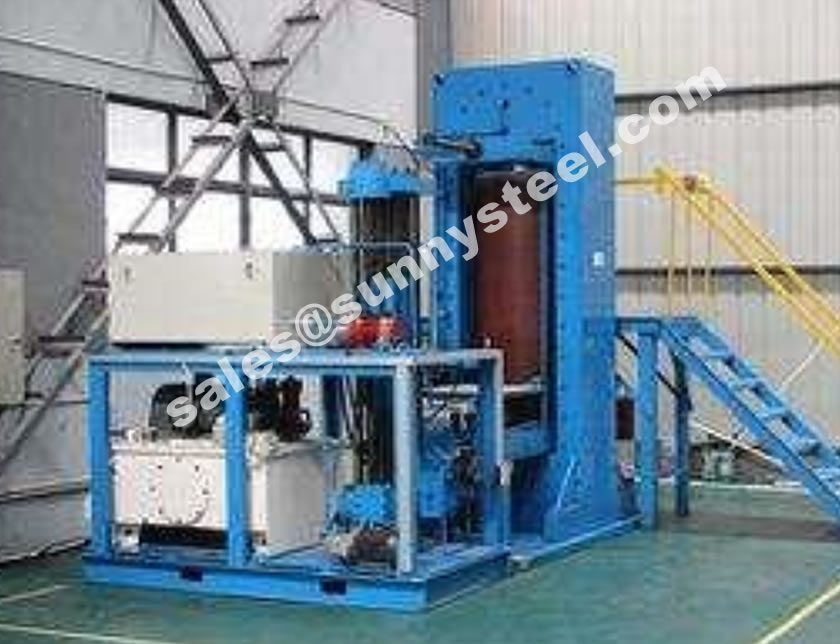
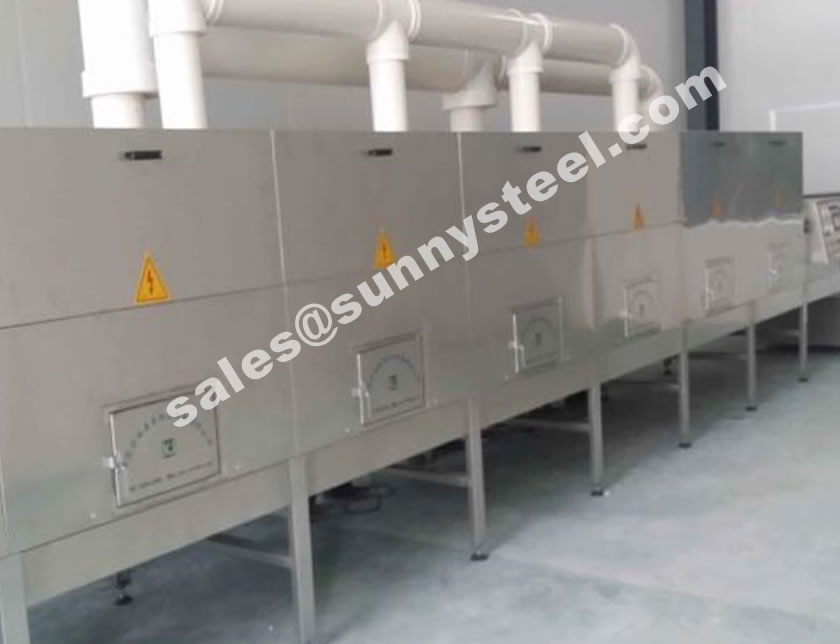
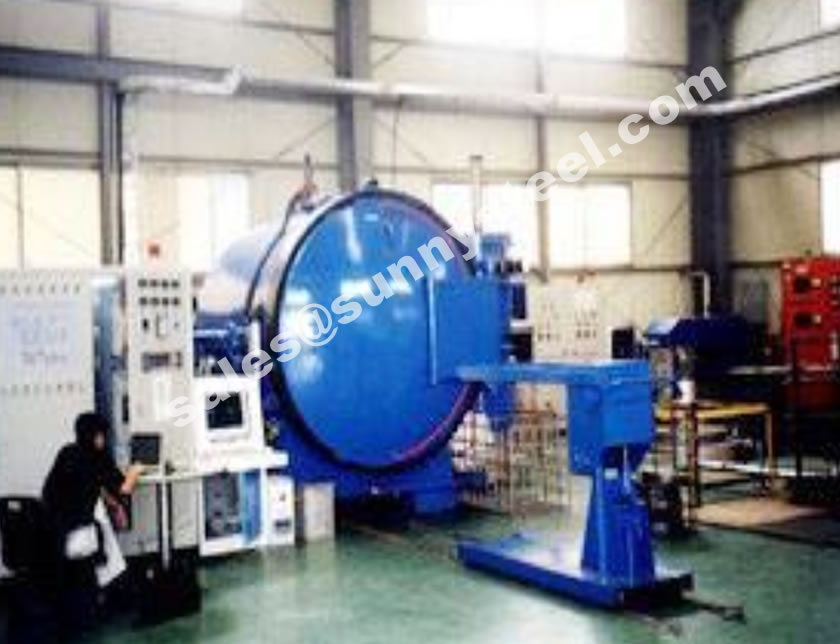
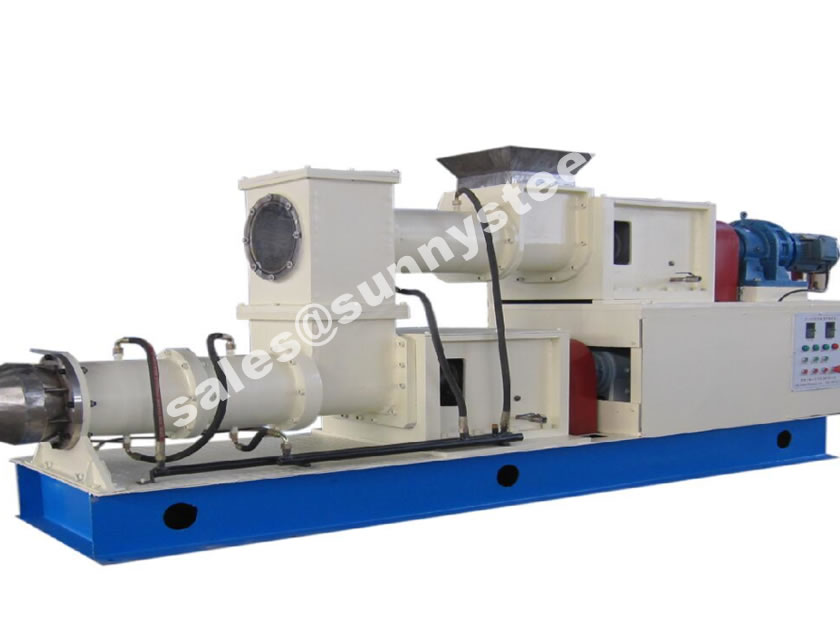






Silicon carbide (SiC) is a lightweight ceramic material with high strength properties comparable to diamond.
Silicon carbide (SiC) is a synthetic crystalline mineral containing silicon and carbon, generally produced in electrical resistance furnaces at high temperatures of 1700 – 2500 °C.
It has excellent thermal conductivity, low thermal expansion and is resisitance form acids. Silicon carbide ceramic is excellent for applications requiring good erosion and abrasive resistance. Consequently, it is useful in a variety of applications including spray nozzles, shot blast nozzles, ceramic tubing and cyclone components.
A mixture of a carbon material and a silica or quartz sand, it is made to react chemically, resulting in the formation of SiC, which develops as a solid cylindrical ingot around the core, with radial layers ranging from graphite in the inside to α-SiC (the highest-grade material with coarse crystalline structure), β-SiC, metallurgical grade and finally un-reacted material on the outside, which is remelted. SiC can be produced in either black or green, depending on the raw materials used.
Once it is cooled, the SiC ingot is sorted accurately and mainly manually by skilled workers and further processed for different applications. The solid SiC material is then carefully crushed, classified, and milled again if necessary. Another option is to further chemically treat the SiC to obtain specific properties for its applications.
Silicon carbide provides benefits for high-temperature, high-voltage and high-power applications.
These include:
Thanks to its versatile properties, silicon carbide is a widely used ceramic material in many high-temperature and wear-resistant applications in many industries, such as:
We produce sintered SiC tubes, reaction bonded SiC tubes and recrystallized SiC tubes. Our recrystallized SiC products have a high purity, while our reaction bonded and sintered silicon carbide tubes have a high mechanical strength. Our silicon carbide tubes possess good wearability,a low thermal expansion coefficient, extreme corrosion resistance, wear resistance, thermal shock resistance, high hardness and self-lubricating properties.
Silicon carbide (SiC) ceramics have a set of unique physical-chemical properties, such as high hardness and mechanical stability at high temperatures, excellent thermal conductivity and low coefficient of thermal expansion, high resistance to corrosion and oxidation, wide bandgap, and others.
| Item | Recrystallized SiC | Sintered SiC | Reaction Bonded SiC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purity of Silicon Carbide | 99.5% | 98% | > 88% |
| Max. Working Temp. (`C) | 1650 | 1550 | 1300 |
| Bulk Density (g/cm3) | 2.7 | 3.1 | > 3 |
| Appearance Porosity | < 15% | 2.5 | 0.1 |
| Flexural strength (MPa) | 110 | 400 | 380 |
| Compressive strength (MPa) | > 300 | 2200 | 2100 |
| Thermal expansion (10^-6/`C) | 4.6 (1200℃) | 4.0 (< 500℃) | 4.4 (< 500℃) |
| Thermal conductivity (W/m.K) | 35~36 | 110 | 65 |
| Main characteristics | High temp. High resistance. High purity |
Fracture Toughness | Chemical Resistance |
Reaction Bonded SiC has the lowest cost production technique with a course grain. Reaction Bonded SiC provides somewhat lower hardness and use temperature, but higher thermal conductivity. Reaction bonded silicon carbide has high strength, high hardness, hig abrasion resistance, high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, good oxidation resistance, good thermal shock resistance, good thermal conductivity, rapid cooling and rapid heat resistance and high temperature creep resistance, etc. It can be made into beam, roller, cooling air pipe, thermocouple protection pipe, temperature measuring pipe, burner nozzle, wear-resisting parts, corrosion-resisting parts, sealing parts and a variety special-shaped structural parts.
Compared with reaction bonded silicon carbide, pressureless sintered silicon carbide has higher purity, better mechanical properties, more prominent corrosion resistance ( Resistantto strong acid and alkali corrosion, It is also the only ceramic material which can resistant to hydrofluoric acid corrosion ), higher wear resistance, because of there’s no free silicon in the material can be used in other materials can not meet the environment, longer service life.
At present, the use of our company’s high wear-resistant ceramic lined steel pipe dozens of thermal power plant practice shows that: ceramic lined steel pipe anti-wear ability, anti-fluid erosion ability.
And it has developed rapidly. When transporting the materials with the harder abrasion (such as ash dregs, slag, coal powder, mining dregs, the rest mines, cement, etc), it will exit the problem that the abrasion of pipes is too rapid. Especially, the abrasion of bent pipes is greatly more rapid.
When transporting the special abrasion materials or erosive materials, it will exit the problem that the damage of pipes is too rapid.
SiC Ceramic lined pipe and the traditional steel pipe, wear-resistant alloy cast steel pipe, cast stone pipe and steel, steel and other rubber pipe is essentially different. Ceramic lined pipe is the outer layer of steel, the inner layer is RBSiC ceramic. Moh’s hardness of up to 13. Wear resistance than carbon steel pipe more than 30 times higher.
In a duct, the elbow wear the fastest, in practice, Ceramic lined pipe used after 1 to 2 years to open the observation and measurement, the composite layer are no obvious wear or tear off, ceramic-coated steel pipe wear Than the thick-walled wear-resistant cast steel pipe increased by nearly 10 times.
Silicon carbide (SiC) is a lightweight ceramic material with high strength properties comparable to diamond. It has excellent thermal conductivity, low thermal expansion, and is resistant to acid corrosion.
Silicon carbide is an excellent ceramic material suitable for applications requiring good corrosion resistance and wear resistance.
Silicon carbide (SiC) ceramics have a set of unique physical-chemical properties, such as high hardness and mechanical stability at high temperatures, excellent thermal conductivity and low coefficient of thermal expansion, high resistance to corrosion and oxidation, wide bandgap, and others.
Sintered Silicon Carbide has demonstrated an excellent performance record as ceramic material in composite armor protection systems. The properties of sintered silicon carbide, such as its high hardness, compressive strength and elastic modulus, provide superior ballistic capability when confronted with high-velocity projectiles. The low specific density of the material makes it suitable in applications where weight requirements are critical.
Sintered Silicon Carbide tubes are used in shell and tube heat exchangers in the chemical process industry. The tubes used in these applications are often over 4 m in length.
Pumps must operate in an infinite variety of demanding environments. Sintered Silicon Carbide offers a high performance seal face material that has proven successful in such diverse pumping applications as chemical processing, refining, mining and pulp and paper processing. The material provides superior corrosion and abrasion resistance; shock resistance; and low sliding friction against a wide range of mating materials.
For state-of-the-art magnetically driven pumps, sintered silicon carbide is particularly suited for thrust and journal bearing components. Excellent corrosion resistance provides optimum performance in many chemical environments. High thermal conductivity minimizes the likelihood of failure due to thermal shock, and its specific strength makes it safe to use at high rotational speeds. Bearing components are usually produced as tight tolerance precision ground parts.
Due to their greater resistance to both wear and thermal shock, sintered silicon carbide seal faces for automotive water pumps are replacing seal faces made of materials such as aluminium oxide. In many cases the material has proven more suitable in meeting the performance demands of U.S. and European vehicles – i.e. lasting the lifetime of the vehicle without leaking. These components are manufactured by conventional high volume pressing and injection moulding methods to meet the economic constraints of the application.
Sintered Silicon Carbide is probably the most popular ceramic alternative to tungsten carbide for blast nozzle applications. Typically providing long life (50% over WC) due to excellent wear and corrosion resistance. The low wear rate maintains the internal nozzle geometry and provides maximum blasting effectiveness, minimum compressor requirements and reduced downtime due to replacement. Sintered silicon carbide is also about one fifth the weight of Tungsten Carbide, so the blasting operation is also easier for the operator. Nozzles are often produced as semi finished (non-ground) components thereby reducing costs.
The outstanding corrosion resistance of sintered silicon carbide, particularly in acids, makes it an ideal candidate for valve and valve trim applications. Typical demanding applications such as slurry flashing, HF acid handling and rare earth processing use sintered silicon carbide valve components.
The excellent corrosion and wear resistance of sintered silicon carbide provides hard surfaces that can be machined to smooth, highly polished finishes. These finishes offer low coefficients of friction and compatibility with forming fabrics. Tiles, inserts and palm guides are available in finished and semi-finished forms.
Often used in applications where tungsten carbide and alumina fail to provide optimum lifetime performance.
The benefit of using silicon carbide for semiconductor components includes; the thermal expansion match to silicon, the resistance to wear and chemical corrosion which leads to reduced maintenance and component recycling. The material is well suited as a structural material for low mass silicon wafer handling components and rigid, dimensionally stable platforms due to its lightness in weight and high elastic modulus. Typical applications include vacuum chucks, chemical mechanical polishing blocks, wafer carriers, and thermocouple protection tubes.
Silicon carbide ceramics are widely used not only in industry, but also in other fields. So, what should be paid attention to when using silicon carbide ceramics?
The hardness of silicon carbide ceramics is very strong, although it does not look as eye-catching as other ceramics, but the use of ornamental ceramics is incomparable. In the process of use, as long as you follow the instructions, there is no need to pay special attention to. Just keep it clean.
If the method used is not correct, the silicon carbide ceramics will be damaged. We can extend its service life by regular maintenance.
Our silicon carbide tube and fitting is carefully handled to minimize damage during storage and transportation and to preserve the quality of our products in their original condition. We guarantee intact during transportation, loading and unloading, and have measures to reduce vibration and impact, so as to ensure the integrity of the product during transportation.
Our Silicon Carbide Tubes (SiC Tubes) are carefully handled to minimize damage during storage and transportation and to preserve the quality of our products in their original condition.
Typical silicon carbide characteristics include:
Typical silicon carbide applications include:
They are used more for operation with wear at low temperature than for high temperature behavior. SiC applications are such as sandblasting injectors, automotive water pump seals, bearings, pump components, and extrusion dies that use high hardness, abrasion resistance, and corrosion resistance of carbide of silicon.
Metallurgy and power industry: The reason why these two industries are put together is mainly because the two industries have a large number of metal pipes for the transmission of coal powder, ash, mud, and the like. After using the wear-resistant elbow pipe, the advantages of strong wear resistance, long life and easy installation are immediately highlighted.
Mining industry: If the wear-resistant elbow pipe is not used, the ordinary pipe is used for the transportation of the ore powder. Due to the filling of the mine and the transportation of the concentrate powder, the wear of the pipe is relatively large, so that the life of these pipes is only about one year. After wearing elbow pipes, the life of such pipes will be extended by a factor of five.
Coal industry: If long-distance wet transport of coal is required, the pipe has the requirements of good wear resistance and high corrosion resistance, and the pipe with wear-resistant elbow can meet these requirements well.
