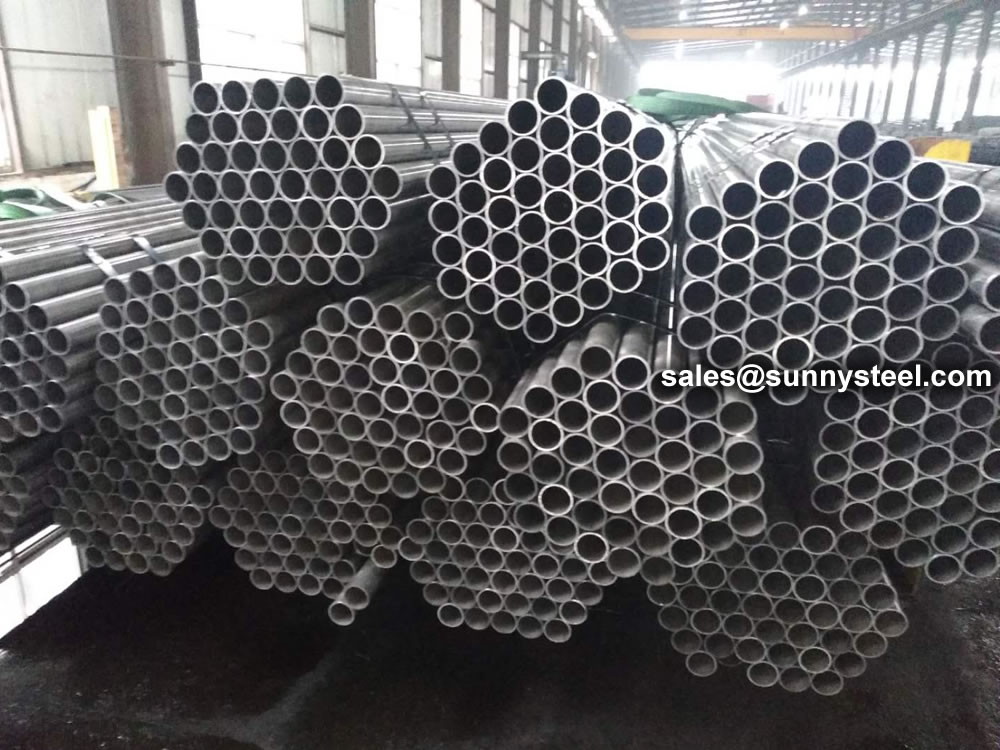
DSAW Pipe
Double Submerged Arc Welded (DSAW) pipes for reliable and strong construction.
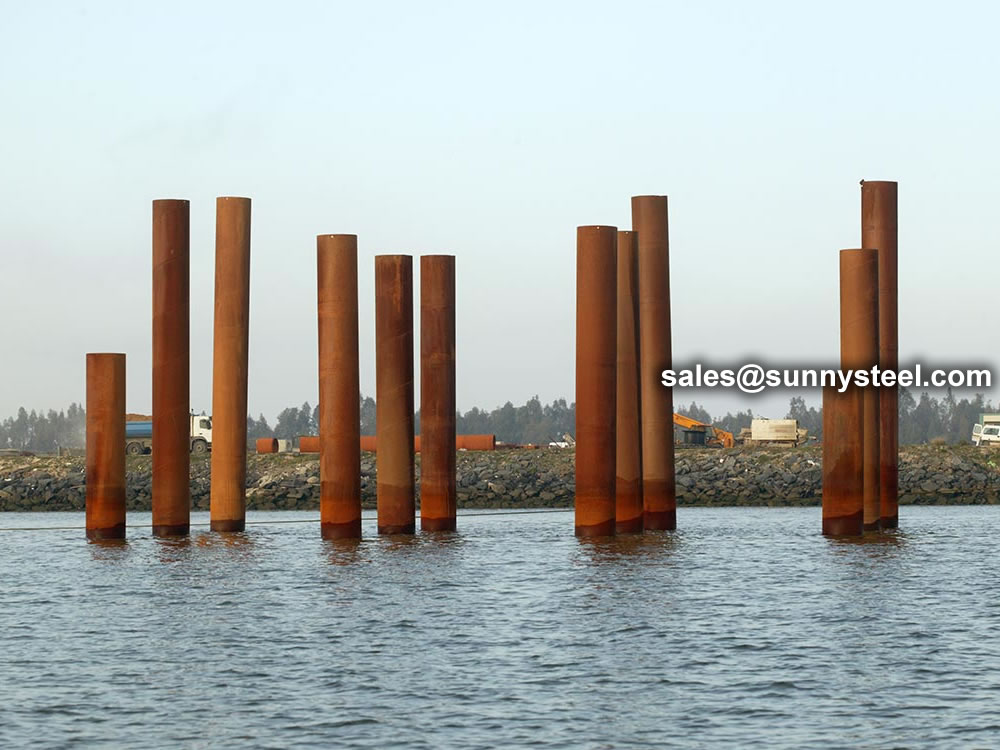

ASTM/ASME A252/SA252 steel piling pipe is a high-quality structural pipe ideally suited for application in various construction projects, including buildings, retaining walls, and other structures requiring solid, dependable steel pipe as its foundational element.
ASTM A252 is the standard specification for steel pipe piles used in construction. These pipe piles are used as load-bearing piles in deep foundation applications or as casing in drilled shafts for construction projects. ASTM A252 pipe piles are designed to withstand high stress and pressure and are available in three grades—Grade 1, Grade 2, and Grade 3—each with different mechanical properties. They are primarily used for structural purposes to support bridges, buildings, marine structures, and other heavy infrastructure.
The ASTM A252 Pipe Pile is an essential component in the construction industry for heavy load-bearing applications. Its versatility, high tensile strength, and durability make it an ideal choice for foundation work in bridges, marine structures, and buildings. For more detailed product specifications or custom requirements, consult a reliable supplier or manufacturer.
ASTM A252 pipe piles are widely used in civil and construction engineering projects. They offer superior structural support and are commonly found in:
| Element | Composition (%) |
|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | ≤ 0.26% |
| Manganese (Mn) | ≤ 1.60% |
| Phosphorus (P) | ≤ 0.05% |
| Sulfur (S) | ≤ 0.05% |
| Grade | Yield Strength (ksi) | Tensile Strength (ksi) |
|---|---|---|
| Grade 1 | 30 | 50 |
| Grade 2 | 35 | 60 |
| Grade 3 | 45 | 66 |
ASTM A252 is a specification that covers welded and seamless steel pipe piles for use in construction and deep foundation projects. These pipes are designed to provide the necessary strength and durability for driving into the ground and supporting heavy loads.
American Standard ASTM A252 is pipe piling material standard that has been widely used in constructions and structural buildings. A252 specification includes three grades (1, 2, and 3), Grade 3 pipe piling material is the most used option.
ASTM A252 is the standard specification for welded and seamless steel pipe piles. It covers the nominal wall thickness of cylinder shape steel pipe, rectangular pipe is not included. These round pipes are used for piling purposes, playing as a permanent role of load carrying and bearing the pressure. Further more, to act as a tank shell to fill with the concrete piles at sight of the project.
This standard stated the values units in inch-pound (also could be translated to SI units), which provides the reference A252 pipe data to engineer or designer, for a strength base of the constructions.
The standard has a limit for element P (phosphorous) maximum 0.050%, since P will make steel fragile, and most important is not good for welding performances. ASTM A252 standard specifications only defines the conten of phosphorous, other elements accord with general carbon steel material.
Considering on the manufacturing types, ASTM A252 pipe piles could be made by seamless or welded processes.
Seamless pipe pile referred as hot rolled or cold drawn and thermal expanded seamless pipe.
Welded pipe pile including ERW (electric resistance welded), flash welded, fusion welded or sub-merged welded SSAW or LSAW. Longitudinal or helical spiral welded.
Raw material iron and steel could be made through the process of Open-hearth, Basic-oxygen, Electric-furnace.
What information would be required before purchase A252 pipe pile
Before purchase the pipe piles under ASTM A252 specification, below information will be required:
a. Quantity in feet, meter, or number of lengths
b. Material Name in steel pipe pile
c. Manufacturing types in seamless or welded (ERW, EFW, LSAW, SSAW)
d. Grades (There are three levels of ASTM A252 Grade 3, 2, and 1)
e. Size (OD and nominal wall thickness, schedule in ASME B36.10)
f. Length in SGL, DGL or fixed length.
g. Ends types beveled or plain ends
h. Inspection related and shipping mark
Generally the surface imperfections that exceed 25% are called defects, and for the defects that do not exceed 22.5% of the nominal wall in depth could be repaired by welding. Before do butt welding for two pipe pile, these defects shall be removed completely.
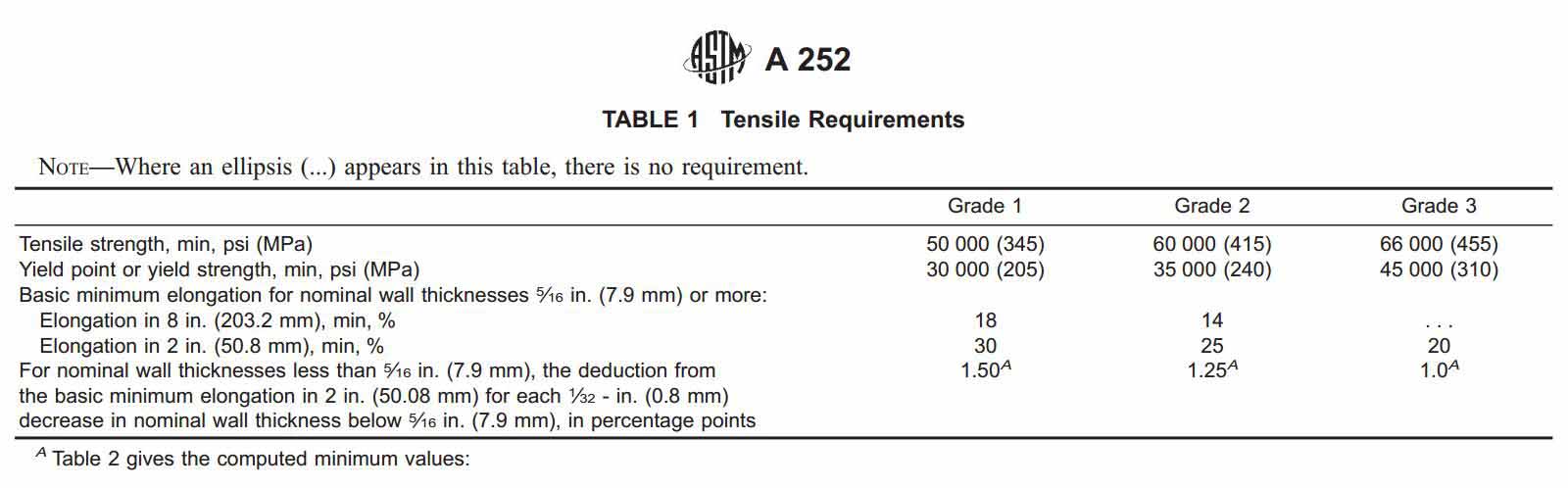
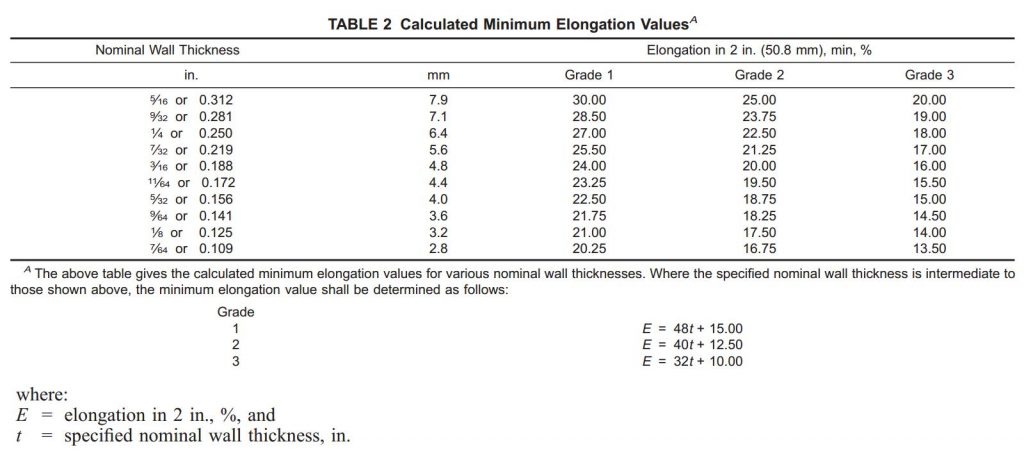
Based on the tensile strength and the yield strength the ASTM A252 is classified into three categories/grades:
a. ASTM A252 Grade 1
b. ASTM A252 Grade 2
c. ASTM A252 Grade 3
In three grades of this standard, ASTM A252 Grade 3 pipe piling is the most common and used in piling activities. Because it has a higher tensile strength (455 Mpa or 66,000 psi) and yield strength (310 Mpa or 45,000 psi).
Testing Requirements for A252 steel pipe piling in seamless and welded
It includes:
Heat Analysis: Limits to elements P, and heat result shall be reported in MTC to customer.
Product Analysis: Test frequency shall be determined by the pipe diameter, where, under 14 inch 2 samples per 200 pieces, 14 to 36 inch 2 samples per 100 pieces, above 36 inch is 2 per 3000 ft.
Tensile requirements: Values shall be complied to the above tensile strength and yield strength. It shall be noted that if got a vague yield point, then to test yield strength corresponding to a permanent offset of 0.2% of the gage length of the sample specimen, or to test a total extension of 0.5% of the gage length under load.
Pipe pile weights per units (Feet, meter or lengths)
Tolerance allowed: A252 pipe pile weight shall be in +15% or -5% of theoretic weight. OD tolerances at +/-1%, wall thickness +/- 12%.
Lengths: As specified SRL, DRL, or fixed length 20 ft or 40 ft and customized.
Hydrostatic test is not specified in ASTM A252 pipe specification, as normally piling pipe is filling with cement and concrete and forming, not for liquid transmission, so hydrotest is not required.
Seamless, welded, (Longitudinal or helical welded) test methods are different. Check ASTM A252 pipe standard specification for more details. But all of these types are tested in a room temperature.
Nowadays pipe piling is developed to a direction with deep distance and big diameters usage, because the constructions, buildings, bridges now is getting higher even super higher. In United States or Japan steel pipe pile length has reached to 100 meter, diameters reach to 2500 mm. And in China even more.















| Product Name | Executive Standard | Dimension (mm) | Steel Code / Steel Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Casting | API 5CT | Ø48.3~273 x WT2.77~11.43 | J55, K55, N80, L80 |
| Tubing | API 5CT | Ø48.3~273 x WT2.77~11.43 | J55, K55, N80, L80, H40 |
| Product Name | Executive Standard | Dimension (mm) | Steel Code / Steel Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Line Pipes | API 5L | Ø60.3~273.1 x WT2.77~12.7 | A25, A, B, X42, X46, X52, X56, X60, X65, X70, X80 |
| Product Name | Executive Standard | Dimension (mm) | Steel Code / Steel Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric-Resistance-Welded Steel Pipes | ASTM A135 | Ø42.2~114.3 x WT2.11~2.63 | A |
| Electric-Resistance-Welded Carbon Steel and Carbon-Manganese Steel Boiler and Superheater Tubes | ASTM A178 | 42.2-114.3 x 2.11-2.63 | A, C, D |
| ERW and Hot-dip Galvanized Steel Pipes | ASTM A53 | Ø21.3~273 x WT2.11~12.7 | A, B |
| Pipes for Piling Usage | ASTM A252 | Ø219.1~508 x WT3.6~12.7 | Gr.2, Gr.3 |
| Tubes for General Structural Purpose | ASTM A500 | Ø21.3~273 x WT2.11~12.7 | Gr.2, Gr.3 |
| Square Pipes for General Structural Purpose | ASTM A500 | 25 x 25~160 x 160 x WT1.2~8.0 | Carbon Steel |
| Product Name | Executive Standard | Dimension (mm) | Steel Code / Steel Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Threaded Steel Pipes | DIN 2440 | Ø21~164 x WT2.65~4.85 | Carbon Steel |
| Product Name | Executive Standard | Dimension (mm) | Steel Code / Steel Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Screwed and Socketed Steel Tubes | BS 1387 | Ø21.4~113.9 x WT2~3.6 | Carbon Steel |
| Scaffolding Pipes | EN 39 | Ø48.3 x WT3.2~4 | Carbon Steel |
| Product Name | Executive Standard | Dimension (mm) | Steel Code / Steel Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel Tubes for General Structure Purpose | JIS G3444 | Ø21.7~216.3 x WT2.0~6.0 | Carbon Steel |
| Carbon Steel Tubes for Machine Structure Purpose | JIS G3445 | Ø15~76 x WT0.7~3.0 | STKM11A, STKM13A |
| Carbon Steel Pipes for Ordinary Piping | JIS G3452 | Ø21.9~216.3 x WT2.8~5.8 | Carbon Steel |
| Carbon Steel Pipes for Pressure Service | JIS G3454 | Ø21.7~216.3 x WT2.8~7.1 | Carbon Steel |
| Carbon Steel Rigid Steel Conduits | JIS G8305 | Ø21~113.4 x WT1.2~3.5 | G16~G104, C19~C75, E19~E75 |
| Carbon Steel Rectangular Pipes for General Structure | JIS G3466 | 16 x 16~150 x 150 x WT0.7~6 | Carbon Steel |
The alloy content of the coil is often lower than similar grades of steel plate, improving the weldability of the spiral welded pipe. Due to the rolling direction of spiral welded pipe coil is not perpendicular to the pipe axis direction, the crack resistance of the spiral welded pipe materials.
Welded steel pipe refers to a steel pipe with seams on the surface that is welded by bending and deforming a steel strip or steel plate into a circular, square or other shape. The blanks used for welded steel pipes are steel sheets or strips.
Since the 1930s, with the rapid development of continuous rolling production of high-quality strip steel and the advancement of welding and inspection technology, the quality of welds has been continuously improved, and the varieties and specifications of welded steel pipes have been increasing.
When the T-shaped welded steel pipe contains Ni, it has strong corrosion resistance in an acidic environment. In an environment containing sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid, the higher the Ni content in the T-shaped welded steel pipe, the stronger the corrosion resistance. Under normal circumstances, only adding Cr to the T-shaped welded steel pipe can prevent the phenomenon of corrosion. The poor edge condition of the strip is another important cause of misalignment. The effects of changes in mass flow, heat flow density and structural parameters (ratio of helical curvature diameter to T-shaped welded steel pipe diameter Dc/D) on the heat transfer coefficient of saturated bubble boiling in vertical spiral pipes.
During the production of T-shaped welded steel pipes, misalignment occurs from time to time, and there are many influencing factors. In production practice, the steel pipe is often degraded by the wrong side and out of tolerance. Therefore, it is necessary to analyze the reasons for the misalignment of the spiral steel pipe and its preventive measures.
Due to the poor shape and dimensional accuracy of the head and tail of the uncut steel strip, it is easy to cause the steel strip to bend hard and cause misalignment during butt joint. Simulation parameter range: vertical pipe: pipe diameter D=10mm, pipe length L=660mm; three types of vertical T-shaped welded steel pipe: pipe diameter D=10mm, the change of the ratio of the curvature diameter of the T-shaped welded steel pipe to the spiral pipe diameter is Dc /D=15, 20, 25, helical pitch Pt=20mm, tube lengths are L=503mm, L=660mm, L=817mm respectively. Mass flow G=200~400Kg/(m'2 s), heat flux density q=5~15KW/m'2, saturation pressure p, saturation=0.414880MPa, saturation temperature T, saturation=283.15K.
The technical requirements and inspection of welded pipes are based on the provisions of the GB3092 "Welded Steel Pipes for Low-Pressure Fluid Transmission". It can be delivered according to fixed length or double length. The surface of the steel pipe should be smooth, and defects such as folds, cracks, delamination, and lap welding are not allowed. The surface of the steel pipe is allowed to have minor defects such as scratches, scratches, weld misalignment, burns and scars that do not exceed the negative deviation of the wall thickness. The thickening of the wall thickness and the presence of inner seam weld bars are allowed at the weld.
Welded steel pipes should be subjected to mechanical performance test, flattening test and flaring test, and must meet the requirements of the standard. When the steel pipe should be able to withstand the internal pressure, carry out a pressure test of 2.5Mpa, and keep it for one minute without leakage. The method of eddy current flaw detection is allowed to replace the hydrostatic test. The eddy current flaw detection is carried out according to the standard of GB7735 "Steel tube eddy current flaw detection inspection method". The eddy current flaw detection method is to fix the probe on the frame, keep a distance of 3~5mm between the flaw detection and the weld seam, and conduct a comprehensive scan of the weld seam by the rapid movement of the steel pipe. The flaw detection signal is automatically processed and sorted by the eddy current flaw detector. To achieve the purpose of flaw detection. The welded pipe after the flaw detection is cut off according to the specified length with a flying saw, and it is rolled off the assembly line through the turning frame. Both ends of the steel pipe should be chamfered with flat ends, printed with marks, and the finished pipes are packed in hexagonal bundles before leaving the factory.
Straight seam steel pipe is a steel pipe whose weld seam is parallel to the longitudinal direction of the steel pipe. Generally, its strength is higher than that of straight seam welded pipe. Narrower billets can be used to produce welded pipes with larger diameters, and the same width of billets can be used to produce welded pipes with different pipe diameters. But compared with the straight seam pipe of the same length, the weld length is increased by 30~100%, and the production speed is lower. So what are its processing methods?
The surface quenching and tempering heat treatment of straight seam welded pipe is usually carried out by induction heating or flame heating. The main technical parameters are surface hardness, local hardness and effective hardened layer depth. Vickers hardness tester can be used for hardness testing, and Rockwell or superficial Rockwell hardness tester can also be used. When the surface heat treatment hardened layer is thick, the Rockwell hardness tester can also be used. When the thickness of the heat-treated hardened layer is 0.4-0.8mm, the HRA scale can be used, and when the thickness of the hardened layer exceeds 0.8mm, the HRC scale can be used.
If the parts require high local hardness, local quenching heat treatment can be carried out by means of induction heating. Such longitudinal welded pipes usually need to mark the location of local quenching heat treatment and local hardness value on the drawing. Hardness testing of longitudinally welded pipes shall be carried out in the area. The hardness testing instrument can use a Rockwell hardness tester to test the HRC hardness value. If the heat-treated hardened layer is shallow, a surface Rockwell hardness tester can be used to test the HRN hardness value.
The three hardness values of Vickers, Rockwell and Superficial Rockwell can be easily converted to each other and converted into hardness values required by standards, drawings or users. The corresponding conversion tables are given in the international standard ISO, the American standard ASTM and the Chinese standard GB/T.
