Pipe elbows
Pipe elbows are versatile pipe fittings used to make turns in piping systems, available in various angles and materials.

Butt weld pipe fittings allow for changing the direction of flow, reducing pipe sizes and attaching auxiliary equipment.
Download PDFA buttweld pipe fitting is a weldable component used in piping systems for various purposes. These fittings are designed to be welded to pipes, providing a secure and durable connection. They serve several functions:
A buttweld fitting is a weldable pipe fitting that allows for change of direction of flow, to branch off, reduce pipe size or attach auxiliary equipment. Forged Steel buttweld fittings are manufactured in accordance with ANSI / ASME B16.9.
Butt weld fittings are available as elbows, tees, caps, reducers and out lets (olets). These fittings are the most common type of welded pipe fittings and are specified by nominal pipe size and pipe schedule. Buttweld fittings use seamless or welded pipe as the starting material and are formed (through multiple processes) to get the shape of elbows, tees and reducers etc. Just as the pipe is sold from Schedule 10 to Schedule 160, butt weld pipe fittings are sold the same way. Welded butt weld fittings are more common in stainless steel due to cost advantage. SCH 10 fittings are also more common in stainless steel butt weld fittings.
Common material for butt weld fittings are A234 WPB (A & C also available), High Yield Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel 304 and 316 and Nickel Alloys.
Buttweld pipe fittings comprise of long radius elbow, concentric reducer, eccentric reducers and tees. They are an important part of industrial piping systems to change direction, branch off or to mechanically join equipment to the system. Buttweld fittings are sold in nominal pipe sizes with specified pipe schedule. BW fitting’s dimensions and tolerances are defined as per ASME standard B16.9.
Butt Weld fittings are also called Welded Pipe fittings. These welded fittings in carbon steel and stainless steel offer many advantages compared to threaded and socket weld fittings. The latter are only available up to 4-inch nominal size whereas butt weld fittings are available in sizes from ½” to 72”. Some of the benefits of Buttweld fittings are mentioned below.
Welded pipe fittings in carbon steel and stainless steel are the joining components that make possible the assembly of valves, pipes and equipment onto the piping system. Welded fittings compliment pipe flanges in any piping system and allows:
A common example using welded pipe fitting is a pipe reduced by concentric reducer, welded to a weld neck flange and connected to equipment. The figure below represents a complete collection of butt welded pipe fittings.
LR 90 Elbow: Fittings that change direction in a piping system are called elbows. The directional change is given in degrees, such as 45 or 90. Long radius 90 degree elbow has the center line of elbow at 1.5 x NPS from elbow end. 3R elbow has center line at 3 x NPS from elbow end.
LR 45 Elbow: Long radius 45 degree elbow changes the direction by 45 degrees.
SR90 Elbow: Short Radius 90 degree elbow is the same as LR90, except for the measurement between end of elbow to the center line is 1 x NPS.
LR 180 degree Bend: Long Radius 180 degree return bend allows complete reversal of flow. The distance between end of elbow and the center line is 3 x NPS.
SR 180 degree Bend: Short Radius 180 degree return bend allows complete reversal of flow but in a much tighter turn. The distance between end of elbow and the center line is 1 x NPS.
Tee: Butt weld pipe Tee allows a 90 degree branch off from a running pipe. This allows for connecting auxiliary equipment to a pipe. A tee is welded on both sides to the pipe; leaving the branch open for branch off.
Reducing Tee: Butt weld reducing tee has a branch that is smaller than the main run. This allows for branching off to a smaller pipe or equipment from the main run.
Concentric Reducer: A concentric Reducer is also called welded concentric coupling. It allows for connecting a large pipe to a smaller pipe by means of welding. A concentric reducer allows a welded connection between two pipes with the same center line.
Eccentric Reducer: An eccentric reducer is also called welded eccentric coupling. It allows for welding a large pipe to a smaller pipe with an offset center line. The offset of the center line in an eccentric reducer is; Offset = 1/2 x (Largest ID - Smallest ID)
Weldolet: A weldolet, also called welding outlet, is a way of connecting a welded connection that is contoured at the bottom to match the contour of the pipe. So one end of the welding outlet is welded on the pipe, whereas the other end is open to be welded to any other pipe or equipment. A welding outlet requires mentioning the size of out let and the "Run Size" of pipe so the contour can match the contour of the pipe. The size of the welding outlet will always be smaller than run size such as 1/2" welding outlet can be used on pipe (run size) 1/2" and bigger.
Welded Stub End: Stub ends are used with lap joint flange to be welded onto the pipe.
All welded pipe fittings have beveled ends to allow for ease of welding. This bevel allows for full penetration weld in most cases.
Welding Bevel acc. to
There are two types of bevels:

Plain Bevel and Compound Bevel.
A butt weld is a type of weld where the ‘butt end’ of the workpiece (pipes or tubes in our business) is welded to another in the same plane circumferentially. Butt welding is the most common type of joint that is used in piping systems. This type of welding is commonly used for pipe joints that do not require assembly or replacement, such as long-distance or underground pipelines.
A butt weld is a simple and versatile design of a welded joint. The butt weld is formed by simply inserting two pieces of metal next to each other and then welding along the weld seam. It is critical that in a butt weld, the surfaces of the workpieces are joined in the same plane and the weld metal remains within the places of the surfaces. The workpieces are therefore almost aligned and do not overlap, in contrast to overlap joints, for example.
Due to its simplicity, butt welding is the most widely used joining technique for a large number of applications in various industrial sectors. This fundamental welding technique has a number of different welding formations that are suitable for different welding thicknesses.
A butt weld pipe fitting is made by the process of hot forming that includes bending and forming to shape. The starting material of butt weld fitting is a pipe that is cut to length, heated and molded into specific shapes by means of dyes. Heat treatment is also done to remove residual stresses and obtain desired mechanical properties. Read the link here to get more in depth detail of butt weld fitting manufacturing.
All butt weld fittings have beveled ends as per ASME B16.25 standard. This helps create full penetration weld without any extra preparation needed for the butt weld fitting.
Butt weld pipe fittings are most commonly available in carbon steel, stainless steel, nickel alloy, aluminum and high yield material. High yield butt weld carbon steel pipe fittings are available in A234-WPB, A234-WPC, A420-WPL6, Y-52, Y-60, Y-65, Y-70. All WPL6 pipe fittings are annealed and are NACE MR0157 and NACE MR0103 compatible.

Fittings are components that are used to connect, join, or adapt different parts of a system, such as pipes, tubes, or hoses. They serve multiple purposes, including:
The choice of fittings depends on the specific requirements of the system, including factors like the type of fluid or gas, pressure, temperature, and the layout of the piping or tubing system. Different industries, such as plumbing, HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning), manufacturing, and construction, rely on fittings to ensure the proper functioning of their systems.
Pipe fitting dimensions are in either metric or Standard English.
Because pipe fitting covers Pipe Fitting Dimensions several aspects, only the most common pipe fitting sizes can be given here. The most applied version is the 90° long radius and the 45° elbow, while the 90° short radius elbow is applied if there is too little space. The function of a 180° elbow is to change direction of flow through 180°. Both, the LR and the SR types have a center to center dimension double the matching 90° elbows. These fittings will generally be used in furnesses or other heating or cooling units.
Some of the standards that apply to buttwelded fittings are listed below. Many organizations such as ASME, ASTM, ISO, MSS, etc. have very well developed standards and specifications for buttwelded fittings. It is always up to the designer to ensure that they are following the applicable standard and company specification, if available, during the design process.
Some widely used pipe fitting standards are as follows:
ASME: American Society for Mechanical Engineers
This is one of the reputed organizations in the world developing codes and standards.
The schedule number for pipe fitting starts from ASME/ANSI B16. The various classifications of ASME/ANSI B16 standards for different pipe fittings are as follows:
ASTM International: American Society for Testing and Materials
This is one of the largest voluntary standards development organizations in the world. It was originally known as the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM).
AWWA: American Water Works Association
AWWA About – Established in 1881, the American Water Works Association is the largest nonprofit, scientific and educational association dedicated to managing and treating water, the world’s most important resource.
ANSI: The American National Standards Institute
ANSI is a private, non-profit organization. Its main function is to administer and coordinate the U.S. voluntary standardization and conformity assessment system. It provides a forum for development of American national standards. ANSI assigns “schedule numbers”. These numbers classify wall thicknesses for different pressure uses.
MSS STANDARDS: Manufacturers Standardization Society
The Manufacturers Standardization Society (MSS) of the Valve and Fittings Industry is a non-profit technical association organized for development and improvement of industry, national and international codes and standards for: Valves, Valve Actuators, Valve Modification, Pipe Fittings, Pipe Hangers, Pipe Supports, Flanges and Associated Seals
Difference between “Standard” and “Codes”:
Piping codes imply the requirements of design, fabrication, use of materials, tests and inspection of various pipe and piping system. It has a limited jurisdiction defined by the code. On the other hand, piping standards imply application design and construction rules and requirements for pipe fittings like adapters, flanges, sleeves, elbows, union, tees, valves etc. Like a code, it also has a limited scope defined by the standard.
Factors affecting standards: “Standards” on pipe fittings are based on certain factors like as follows:
BSP: British Standard Pipe
BSP is the U.K. standard for pipe fittings. This refers to a family of standard screw thread types for interconnecting and sealing pipe ends by mating an external (male) with an internal (female) thread. This has been adopted internationally. It is also known as British Standard Pipe Taper threads (BSPT )or British Standard Pipe Parallel (Straight) threads (BSPP ). While the BSPT achieves pressure tight joints by the threads alone, the BSPP requires a sealing ring.
JIS: Japanese Industrial Standards
This is the Japanese industrial standards or the standards used for industrial activities in Japan for pipe, tube and fittings and published through Japanese Standards Associations.
NPT: National Pipe Thread
National Pipe Thread is a U.S. standard straight (NPS) threads or for tapered (NPT) threads. This is the most popular US standard for pipe fittings. NPT fittings are based on the internal diameter (ID) of the pipe fitting.
BOLTS & NUTS
We are manufacturer of Flange bolts & Nuts and supply high quality
AN: Here, “A” stands for Army and “N” stands for Navy
The AN standard was originally designed for the U.S. Military. Whenever, a pipe fitting is AN fittings, it means that the fittings are measured on the outside diameter of the fittings, that is, in 1/16 inch increments.
For example, an AN 4 fitting means a fitting with an external diameter of approximately 4/16″ or ¼”. It is to be noted that approximation is important because AN external diameter is not a direct fit with an equivalent NPT thread.
Dash (-) size
Dash size is the standard used to refer to the inside diameter of a hose. This indicates the size by a two digit number which represents the relative ID in sixteenths of an inch. This is also used interchangeably with AN fittings. For example, a Dash “8” fitting means an AN 8 fitting.
ISO: International Organization for Standardization
ISO is the industrial pipe, tube and fittings standards and specifications from the International Organization for Standardization. ISO standards are numbered. They have format as follows:
“ISO[/IEC] [IS] nnnnn[:yyyy] Title” where
| Standard | Specification |
|---|---|
| ASTM A234 | Standard Specification for Piping Fittings of Wrought Carbon Steel and Alloy Steel for Moderate and High Temperature Service |
| ASTM A420 | Standard Specification for Piping Fittings of Wrought Carbon Steel and Alloy Steel for Low-Temperature Service |
| ASTM A234 WPB | ASTM A234 WPB refers to a specific grade of carbon steel pipe fittings, which are widely used in pressure piping and pressure vessel fabrication for service at moderate and elevated temperatures. |
| ASME B16.9 | ASME B16.9 Standard covers overall dimensions, tolerances,ratings, testing, and markings for factory-made wrought buttwelding fittings in sizes NPS 1⁄2 through NPS 48 (DN 15 through DN 1200). |
| ASME B16.28 | ASME B16.28 Standard covers ratings, overall dimensions, testing, tolerances, and markings for wrought carbon and alloy steel buttwelding short radius elbows and returns. |
| MSS SP-97 | MSS SP-97 Standard Practice covers essential dimensions, finish, tolerances, testing, marking, material, and minimum strength requirements for 90 degree integrally reinforced forged branch outlet fittings of buttwelding, socket welding, and threaded types. |
| ASTM A403 | Standard Specification for Wrought Austenitic Stainless Steel Piping Fittings. |
| DIN | EN | ASME |
|---|---|---|
| St 35.8 I St 35.8 III 15 Mo 3 13 CrMo 4 4 10 CrMo 9 10 St 35 N St 52.0 St 52.4 |
P235GH-TC1 P235GH-TC2 16Mo3 13CrMo4-5 10CrMo9-10 X10CrMoVNb9-1 P215NL P265NL L360NB L360NE P355N P355NL1 P355NH |
WPB WPL6 WPL3 WPHY 52 WP11 WP22 WP5 WP9 WP91 WP92 |
ASTM A234/A234M is a standard specification for piping fittings of wrought carbon steel and alloy steel for moderate and high-temperature service. This specification covers several grades of fittings that are used in various applications in the oil and gas, petrochemical, and power generation industries.
Download PDF| Grade | Type | C | Si | S | P | Mn | Cr | Ni | Mo | Other | ób | ós | δ5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WPB | 0.3 | 0.1min | 0.058 | 0.05 | 0.29-1.06 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.15 | V:0.06;Nb:0.02 | 415-585 | 240 | 22 | 197 |
| WPC | 0.35 | 0.1min | 0.058 | 0.05 | 0.29-1.06 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.15 | V:0.06;Nb:0.02 | 485-655 | 275 | 22 | 197 |
| WP1 | 0.28 | 0.1-0.5 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.3-0.9 | 0.44-0.65 | 380-550 | 205 | 22 | 197 | |||
| WP12 CL1 | 0.05-0.2 | 0.6 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.3-0.8 | 0.8-1.25 | 0.44-0.65 | 415-585 | 220 | 22 | 197 | ||
| WP12 CL2 | 0.05-0.2 | 0.6 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.3-0.8 | 0.8-1.25 | 0.44-0.65 | 485-655 | 275 | 22 | 197 | ||
| WP11 CL1 | 0.05-0.15 | 0.5-1 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.3-0.6 | 1-1.5 | 0.44-0.65 | 415-585 | 205 | 22 | 197 | ||
| WP11 CL2 | 0.05-0.2 | 0.5-1 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.3-0.8 | 1-1.5 | 0.44-0.65 | 485-655 | 275 | 22 | 197 | ||
| WP11 CL3 | 0.05-0.2 | 0.5-1 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.3-0.8 | 1-1.5 | 0.44-0.65 | 520-690 | 310 | 22 | 197 | ||
| WP22 CL1 | 0.05-0.15 | 0.5 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.3-0.6 | 1.9-2.6 | 0.87-1.13 | 415-585 | 205 | 22 | 197 | ||
| WP22 CL3 | 0.05-0.15 | 0.5 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.3-0.6 | 1.9-2.6 | 0.87-1.13 | 520-690 | 310 | 22 | 197 | ||
| WP5 CL1 | 0.15 | 0.5 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.3-0.6 | 4-6 | 0.44-0.65 | 415-585 | 205 | 22 | 217 | ||
| WP5 CL3 | 0.15 | 0.5 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.3-0.6 | 4-6 | 0.44-0.65 | 520-690 | 310 | 22 | 217 | ||
| WP9 CL1 | 0.15 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.3-0.6 | 8-10 | 0.9-1.1 | 415-585 | 205 | 22 | 217 | ||
| WP9 CL3 | 0.15 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.3-0.6 | 8-10 | 0.9-1.1 | 520-690 | 310 | 22 | 217 | ||
| WPR | 0.2 | 0.05 | 0.045 | 0.4-1.06 | 1.6-2.24 | 435-605 | 315 | 22/28 | 217 | ||||
| WP91 | 0.08-0.12 | 0.2-0.5 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.3-0.6 | 8-9.5 | 0.4 | 0.85-1.05 | See sdandard | 585-760 | 415 | 20 | 248 |
| WP911 | 0.09-0.13 | 0.1-0.5 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.3-0.6 | 8.5-10.5 | 0.4 | 0.9-1.1 | See sdandard | 620-840 | 440 | 20 | 248 |
For each reduction of 0.01% below the specified C maximum, an increase of 0.06% Mn above the specified maximum will be permitted, up to a maximum of 1.35%.
The sum of Cu, Ni, Cr, and Mo shall not exceed 1.00%.
The sum of Cr and Mo shall not exceed 0.32%.
The maximum carbon equivalent (C.E.) shall be 0.50, based on heat analysis and the formula C.E.=C+Mn/6+(Cr+Mo+V)/5+(Ni+Cu)/15.
| Tensile Requirements | WPB | WPC, WP11CL2 | WP11CL1 | WP11CL3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength, min, ksi[MPa] (0.2% offset or 0.5% extension-under-load) |
60-85 [415-585] |
70-95 [485-655] |
60-85 [415-585] |
75-100 [520-690] |
| Yield Strength, min, ksi[MPa] | 32 [240] |
40 [275] |
30 [205] |
45 [310] |
ASTM A403 Stainless Steel Pipe Fittings refers to the material of forged and rolled austenitic stainless fittings for pressure pipes. Common grades are WP304/L, WP316/L. They can be used into many fields as engineering industry, energy conversion plants etc.
ASTM A403 Standard specification covers the standard for wrought austenitic stainless steel fittings for pressure piping applications.
| Steel No. | Type | C | Si | S | P | Mn | Cr | Ni | Mo | Other | ób | ós | δ5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WP304 | 0.08 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 18-20 | 8-11 | 515 | 205 | 28 | |||
| WP304H | 0.04-0.1 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 18-20 | 8-11 | 515 | 205 | 28 | |||
| WP304L | 0.035 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 18-20 | 8-13 | 485 | 170 | 28 | |||
| WP304LN | 0.03 | 0.75 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 18-20 | 8-10.5 | N2:0.1-0.16 | 515 | 205 | 28 | ||
| WP304N | 0.08 | 0.75 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 18-20 | 8-11 | N2:0.1-0.16 | 550 | 240 | 28 | ||
| WP309 | 0.15 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 22-24 | 12-15 | 515 | 205 | 28 | |||
| WP310 | 0.15 | 1.5 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 24-26 | 19-22 | 515 | 205 | 28 | |||
| WP316 | 0.08 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 16-18 | 10-14 | 2-3 | 515 | 205 | 28 | ||
| WP316H | 0.04-0.1 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 16-18 | 10-14 | 2-3 | 515 | 205 | 28 | ||
| WP316LN | 0.03 | 0.75 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 16-18 | 11-14 | 2-3 | N2:0.1-0.16 | 515 | 205 | 28 | |
| WP316L | 0.035 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 16-18 | 10-16 | 2-3 | 485 | 170 | 28 | ||
| WP316N | 0.08 | 0.75 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 16-18 | 11-14 | 2-3 | N2:0.1-0.16 | 550 | 240 | 28 | |
| WP317 | 0.08 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 18-20 | 11-15 | 3-4 | 515 | 205 | 28 | ||
| WP317L | 0.03 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 18-20 | 11-15 | 3-4 | 515 | 205 | 28 | ||
| WP321 | 0.08 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 17-20 | 9-13 | Ti:5C-0.7 | 515 | 205 | 28 | ||
| WP321H | 0.04-0.1 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 17-20 | 9-13 | Ti:4C-0.7 | 515 | 205 | 28 | ||
| WP347 | 0.08 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 17-20 | 9-13 | Nb+Ta:10C-1.1 | 515 | 205 | 28 | ||
| WP347H | 0.04-0.1 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 17-20 | 9-13 | Nb+Ta:8C-1 | 515 | 205 | 28 | ||
| WP348 | 0.08 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 17-20 | 9-13 | Ta:0.1 | 515 | 205 | 28 | ||
| WP348H | 0.04-0.1 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.045 | 2 | 17-20 | 9-13 | Ta:0.1 | 515 | 205 | 28 |
For each reduction of 0.01% below the specified C maximum, an increase of 0.06% Mn above the specified maximum will be permitted, up to a maximum of 1.35%.
The sum of Cu, Ni, Cr, and Mo shall not exceed 1.00%.
The sum of Cr and Mo shall not exceed 0.32%.
The maximum carbon equivalent (C.E.) shall be 0.50, based on heat analysis and the formula C.E.=C+Mn/6+(Cr+Mo+V)/5+(Ni+Cu)/15.
| Grade | UNS | Tensile Strength, min | Yield Strength,min | Elongation min % in 4D | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ksi | MPa | ksi | MPa | Longit % | Trans% | ||
| ALL | ALL | 75 | 515 | 30 | 205 | 28 | 20 |
| 304L | S30403 | 70 | 485 | 25 | 170 | 28 | 20 |
| 316L | S31603 | 70 | 485 | 25 | 170 | 28 | 20 |
| 304N | S30451 | 80 | 550 | 35 | 240 | 28 | 20 |
| 316N | S31651 | 80 | 550 | 35 | 240 | 28 | 20 |
| S31726 | 80 | 550 | 35 | 240 | 28 | 20 | |
| XM-19 | S20910 | 100 | 690 | 55 | 380 | 28 | 20 |
| S31254 | 94-119 | 650-820 | 44 | 300 | 28 | 20 | |
| S34565 | 115 | 795 | 60 | 415 | 28 | 20 | |
| S33228 | 73 | 500 | 27 | 185 | 28 | 20 | |
Material Furnished to this specification shall conform to the requirements of specifications A960/A960M including any supplementary requirements that are indicates in the purchase order. Failure to company with the common requirements of Specification A960/A960M constitutes non-conformance with this specification . In case of conflict between this specification and Specification A960/A960M , this specification shall prevail.
Material Furnished to this specification shall conform to the requirements of specifications A960/A960M including any supplementary requirements that are indicates in the purchase order. Failure to company with the common requirements of Specification A960/A960M constitutes non-conformance with this specification. In case of conflict between this specification and Specification A960/A960M , this specification shall prevail.
The standard includes several grades of austenitic stainless steel alloys, and uses the WP or CR prefix to mark the grade of steel, depending on the applicable ASTM or MSS size and rated pressure standards. ASTM A403 is designed for forged steel pipe fittings, Cast pipe fittings are not suitable.
| Elements | WPL6, % | WPL9, % | WPL3, % | WPL8, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon [C] | ≤0.30 | ≤0.20 | ≤0.20 | ≤0.13 |
| Manganese [Mn] | 0.50-1.35 | 0.40-1.06 | 0.31-0.64 | ≤0.90 |
| Phosphorus [P] | ≤0.035 | ≤0.030 | ≤0.05 | ≤0.030 |
| Sulfur [S] | ≤0.040 | ≤0.030 | ≤0.05 | ≤0.030 |
| Silicon [Si] | 0.15-0.40 | … | 0.13-0.37 | 0.13-0.37 |
| Nickel [Ni] | ≤0.40 | 1.60-2.24 | 3.2-3.8 | 8.4-9.6 |
| Chromium [Cr] | ≤0.30 | ... | ... | ... |
| Molybdenum [Mo] | ≤0.12 | ... | ... | ... |
| Copper [Cu] | ≤0.40 | 0.75-1.25 | … | … |
| Columbium [Cb] | ≤0.02 | ... | ... | ... |
| Vanadium[V] | ≤0.08 | ... | ... | ... |
*For grade WPL6, the limit for Columbium may be increased up to 0.05% on heat analysis and 0.06% on product analysis.
*Fittings of WPL3 made from plate or forgings may have 0.90 % max manganese.
*Fittings of WPL8 made from plate may have 0.98 % max manganese.
| ASTM A420/ A420M | Tensile Strength, min. | Yield Strength, min. | Elongation %, min | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade | ksi | MPa | ksi | MPa | Longitudinal | Transverse |
| WPL6 | 65-95 | 415-655 | 35 | 240 | 22 | 12 |
| WPL9 | 63-88 | 435-610 | 46 | 315 | 20 | … |
| WPL3 | 65-90 | 450-620 | 35 | 240 | 22 | 14 |
| WPL8 | 100-125 | 690-865 | 75 | 515 | 16 | … |
*All the elongation values are on the basis of standard round specimen, or small proportional specimen, min % in 4 D.
ASTM A234 is Standard Specification for steel pipe fittings includes carbon and alloy steel material for moderate and high temperature services.
ASME B16.9 Standard covers overall dimensions, tolerances,ratings, testing, and markings for factory-made wrought buttwelding fittings in sizes NPS 1⁄2 through NPS 48 (DN 15 through DN 1200).
Download PDF| Nominal | Outside Diameter | 90° Elbows | 45° Elbows | 180° Returns | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pipe Size |
Long Radius | Short Radius | Long Radius | Long Radius | ||||
| (inches) | (mm) | (inches) | Center to Face | Center to Face | Center to Face | Radius | Center to Center | Back to face |
| (inches) | (inches) | (inches) | (inches) | (inches) | (inches) | |||
| 1/2 | 21.3 | 0.84 | 1.5 | – | 5/8 | 2 | 1.875 | |
| 3/4 | 26.7 | 1.05 | 1.125 | – | 7/16 | 2.25 | 1.6875 | |
| 1 | 33.4 | 1.315 | 1.5 | 1 | 7/8 | 3 | 2.1875 | |
| 1.25 | 42.2 | 1.66 | 1.875 | 1.25 | 1 | 3.75 | 2.75 | |
| 1.5 | 48.3 | 1.9 | 2.25 | 1.5 | 1.125 | 3 | 4.5 | 3.25 |
| 2 | 60.3 | 2.375 | 3 | 2 | 1.375 | 4 | 6 | 4.1875 |
| 2.5 | 73 | 2.875 | 3.75 | 2.5 | 1.75 | 5 | 7.5 | 5.1875 |
| 3 | 88.9 | 3.5 | 4.5 | 3 | 2 | 6 | 9 | 6.25 |
| 3.5 | 101.6 | 4 | 5.25 | 3.5 | 2.25 | 7 | 10.5 | 7.25 |
| 4 | 114.3 | 4.5 | 6 | 4 | 2.5 | 8 | 12 | 8.25 |
| 5 | 141.3 | 5.563 | 7.5 | 5 | 3.125 | 10 | 15 | 10.3125 |
| 6 | 168.3 | 6.625 | 9 | 6 | 3.75 | 12 | 18 | 12.3125 |
| 8 | 219.1 | 8.625 | 12 | 8 | 5 | 12 | 24 | 16.3125 |
| 10 | 273.1 | 10.75 | 15 | 10 | 6.25 | 15 | 30 | 20.375 |
| 12 | 323.9 | 12.75 | 18 | 12 | 7.5 | 18 | 36 | 24.375 |
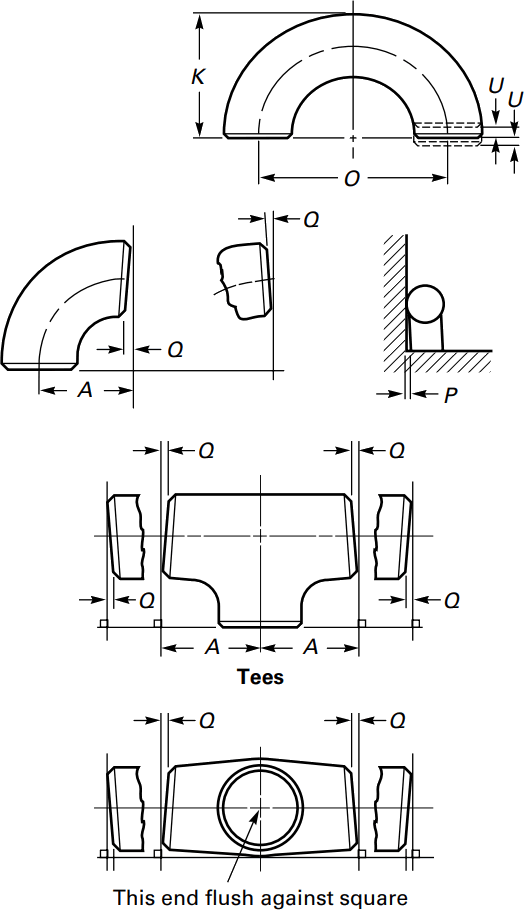
| NOMINAL PIPE SIZE NPS | ANGULARITY TOLERANCES | ANGULARITY TOLERANCES |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Off Angle Q | Off Plane P |
| ½ to 4 | 0.03 | 0.06 |
| 5 to 8 | 0.06 | 0.12 |
| 10 to 12 | 0.09 | 0.19 |
| 14 to 16 | 0.09 | 0.25 |
| 18 to 24 | 0.12 | 0.38 |
| 26 to 30 | 0.19 | 0.38 |
| 32 to 42 | 0.19 | 0.5 |
| 44 to 48 | 0.18 | 0.75 |
All dimensions are given in inches. Tolerances are equal plus and minus except as noted.
The ASME B16.9 pipe fittings can be used under the jurisdiction of the ASME Boiler & Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC) as well as the ASME Code for pressure piping. Referencing pressure ratings of flanges per ASME B16.5, they can be designated as Classes 150, 300, 600, 900, 1500 and 2500. The allowable pressure ratings for ASME B16.9 pipe fittings may be calculated as for straight seamless pipe of equivalent material in accordance with the rules established in the applicable sections of ASME B31 Code for pressure piping.
The design of butt welding pipe fittings made to ASME B16.9 shall be established by one of the following methods: (a) mathematical analyses contained in pressure vessel or piping codes; (b) proof testing; (c) experimental stress analysis with hydrostatic testing to validate experimental results; (d) detailed stress analysis with results evaluation.
Generally, ASME B16.9 pipe fittings shall be marked to show the following details: “trademark + material grade + wall thickness + size + heat number”. For example, “M ASTM A234 WP5 SCH80 6″ 385“. When steel stamps are used, care shall be taken so that
the marking is not deep enough or sharp enough to cause cracks or to reduce the wall thickness of the fitting below the minimum allowed.
The ASME B16.9 fittings may be made from an extensive range of mateirals covering (1) carbon and low-alloy steels in accordance with ASTM A234 and ASTM A420; (2) austenitic and duplex stainless steels in accordance with ASTM A403 and ASTM A815; (3) nickel alloys in accordance with ASTM B366; (4) aluminum alloys in accordance with ASTM B361; and (5) titanium alloys in accordance with ASTM B363.
Sizes 1/2″ – 48″
MSS SP-97 Standard Practice covers essential dimensions, finish, tolerances, testing, marking, material, and minimum strength requirements for 90 degree integrally reinforced forged branch outlet fittings of buttwelding, socket welding, and threaded types.
| Elements | Value, % |
|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | ≤0.30 |
| Manganese (Mn) | ≤1.60 |
| Phosphorus (P) | ≤0.035 |
| Sulfur (S) | ≤0.035 |
| Copper (Cu) | ≤0.50 |
| Nickel (Ni) | ≤0.50 |
| Silicon (Si) | ≤0.50 |
| Chromium (Cr) | ≤0.25 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | ≤0.13 |
| Vanadium (V) | ≤0.13 |
| Columbium (Cb) | ≤0.10 |
| Titanium(Ti) | ≤0.05 |
*1. The sum of Cu, Ni, Cr and Mo shall not exceed 1%.
*2. Carbon equivalent C.E.=C+Mn/6+(Cr+Mo+V)/5+(Ni+Cu)/15 shall not exceed 0.45%.
A Weldolet is a type of pipe fitting used for branch connections on pipes.
It is designed to fit over the run pipe and be welded onto it, with a branch pipe connected to the other end. This creates a strong and permanent connection between the pipes, making it an efficient and durable solution for piping systems.
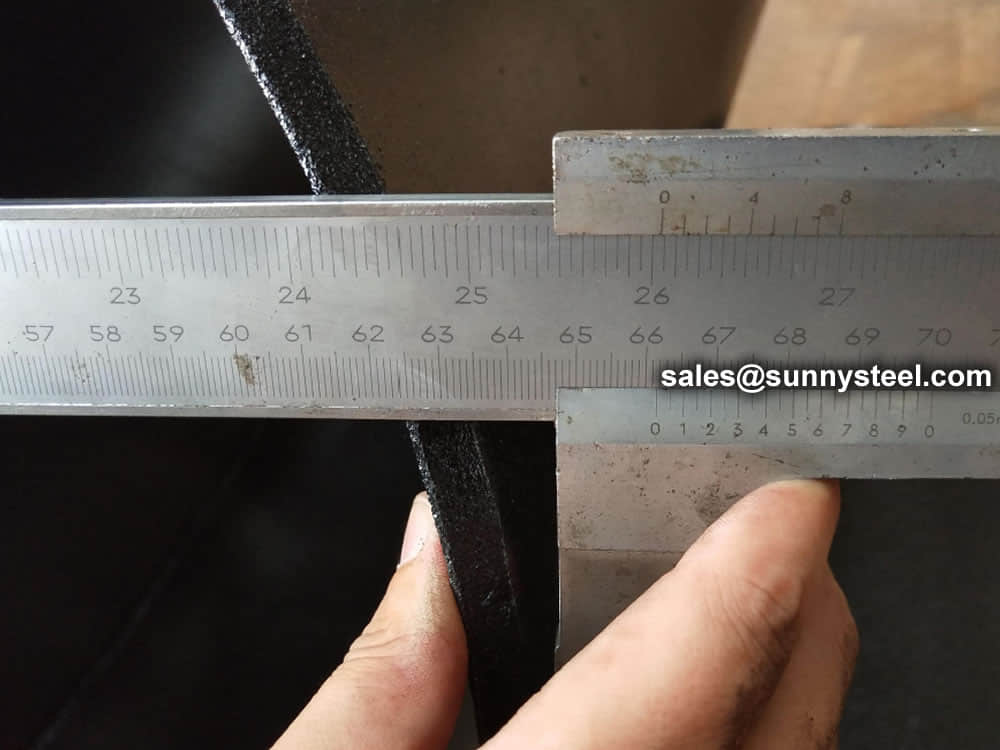
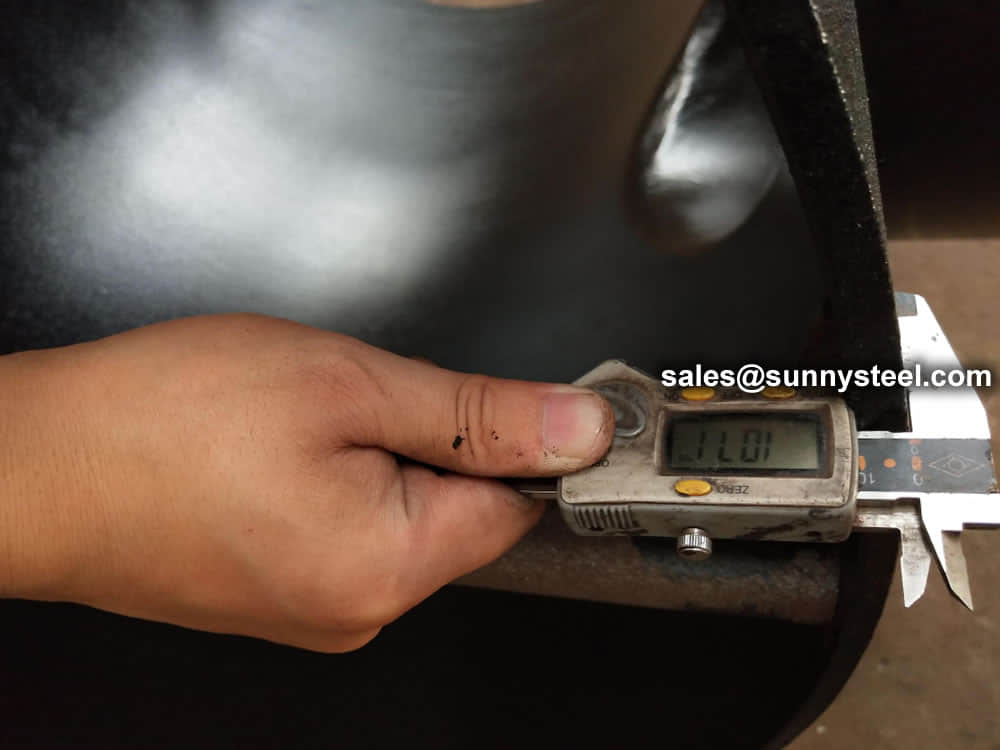
Visual Inspection is conducted on fittings to check any surface imperfections. Both fittings body and weld are checked for any visible surface imperfections such as dents, die marks, porosity, undercuts, etc. Acceptance as per applicable standard.
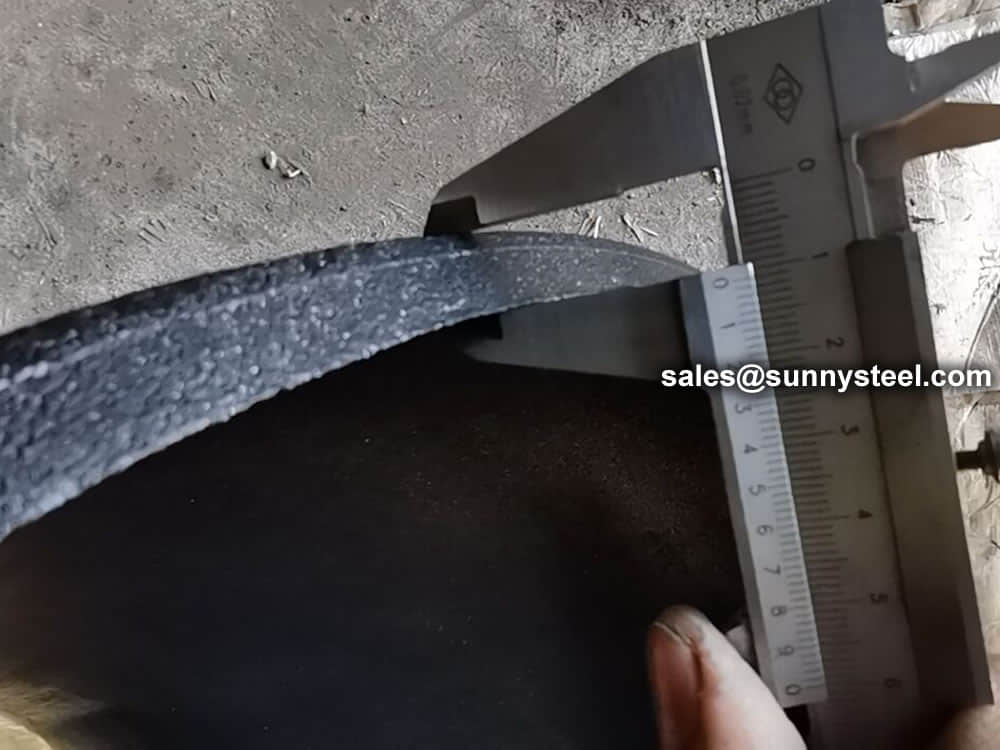
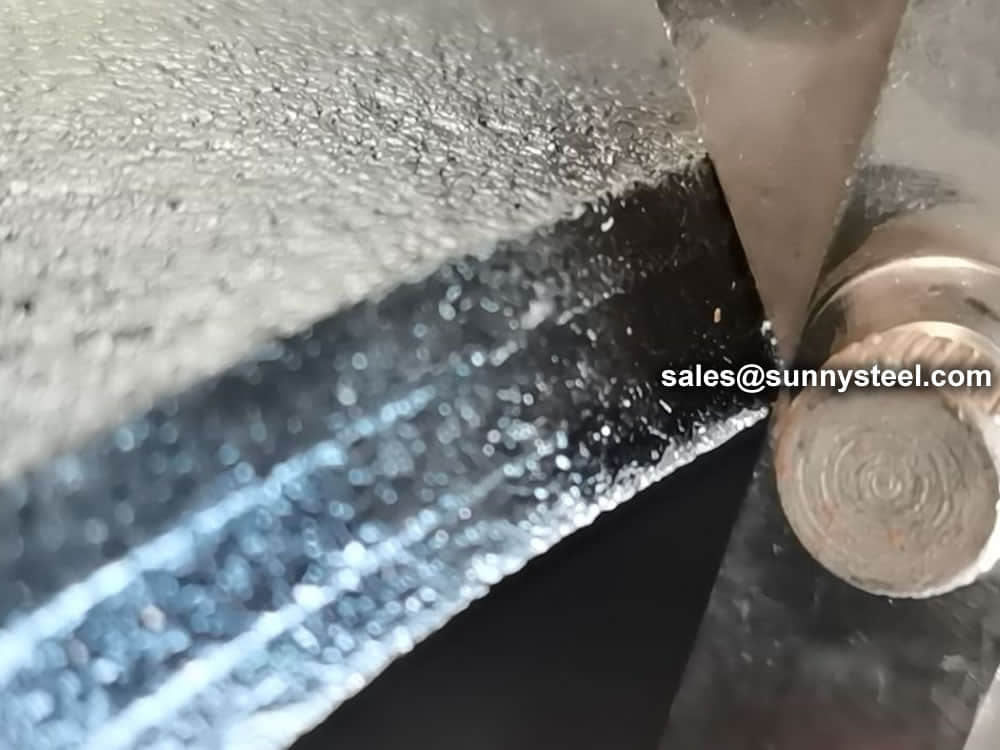
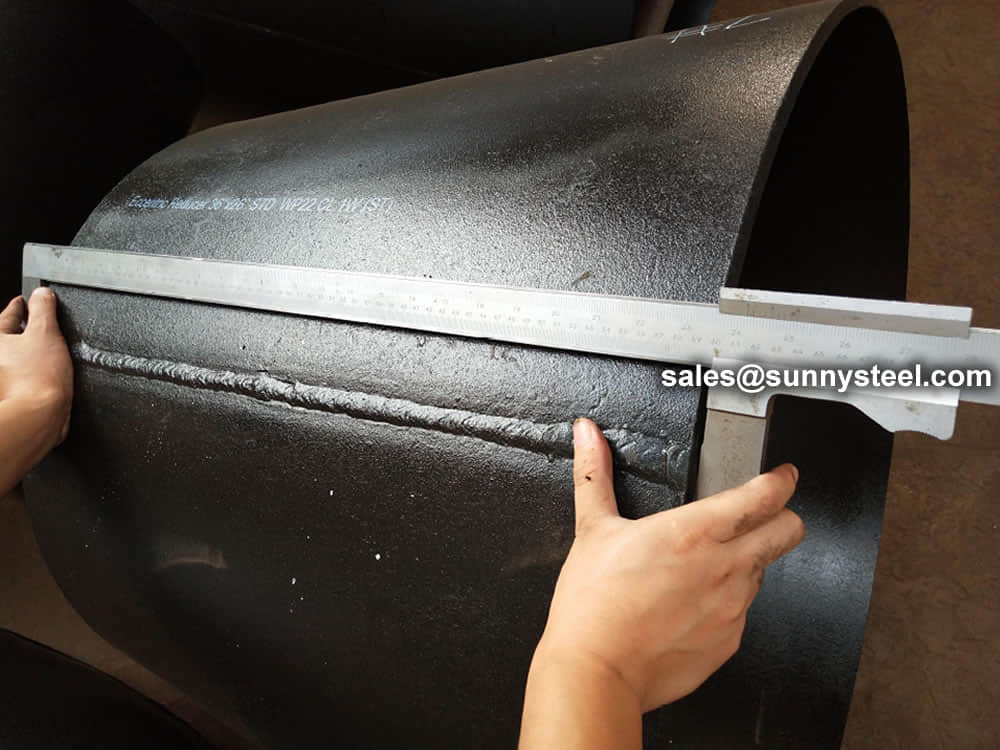
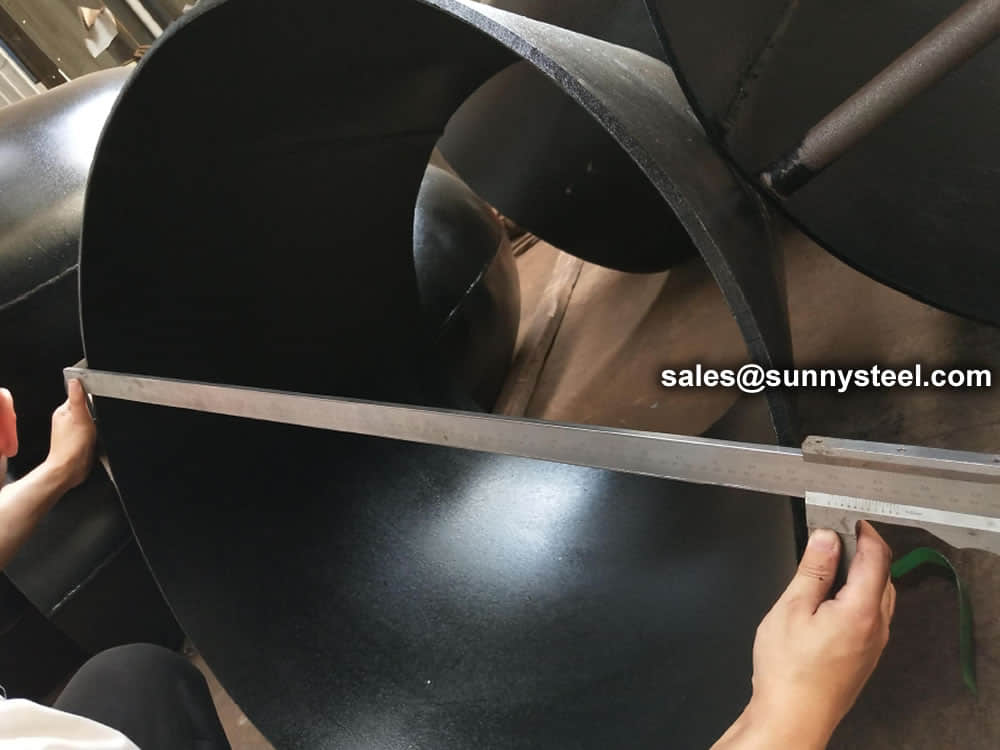









For packing of carbon steel flanges with painting,we would use the bubble wrap to protect the painting.For flanges without painting or oiled with long-term shipment,we would suggest client to use the anti-tarnish paper and plastic bag to prevent the rust.
