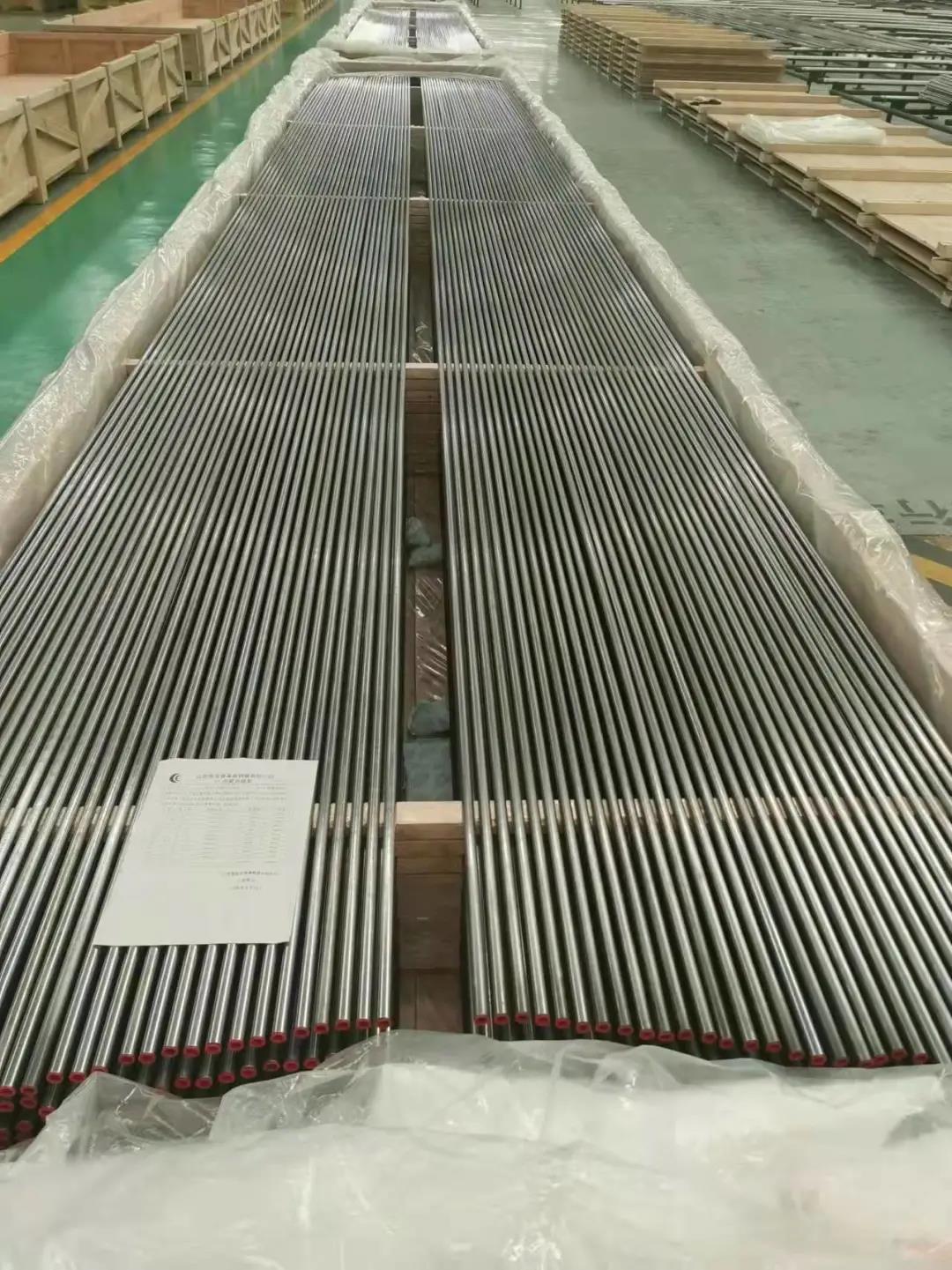
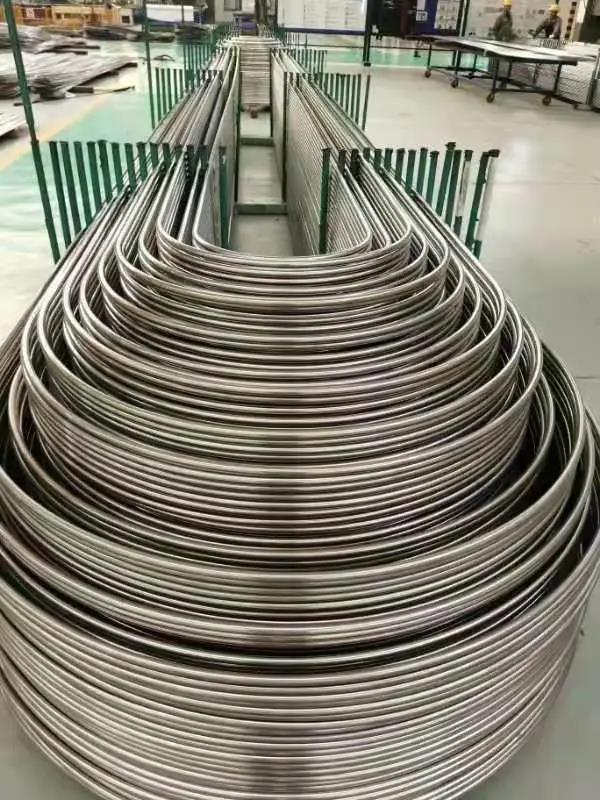
Stainless U bend tubes
Stainless U bend tubes are made of stainless steel and are bent in a U-shape to redirect the flow of liquids or gases in a piping system.
U Bend tube heat exchangers designed for high temperature applications, especially steam condensing or hot oil systems.
Each U bend tube of our range is rigorously quality checked by our team of talented professionals on every stage of production to deliver the clients defect free best quality products.

We bring forth an exclusive range of U-bend tubes, which are known for their superior quality and excellent functionality.
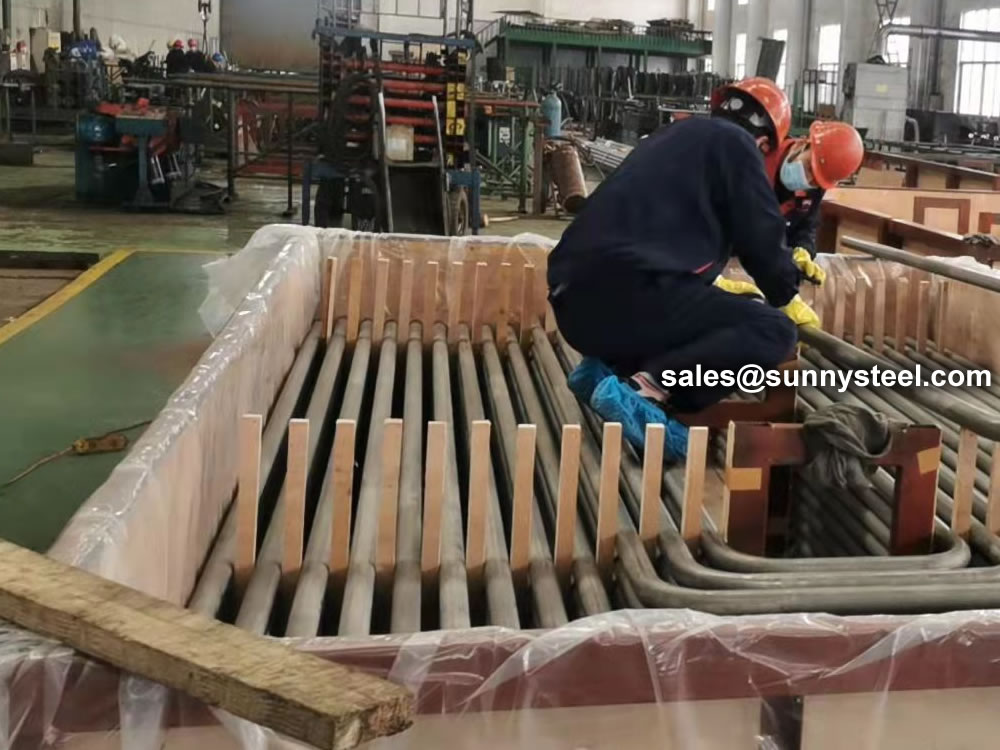
After U bend (cold forming), heat treatment of bending portion may be required. Temperature is controlled through the entire heat treated area by fixed and portable infrared pyrometers.
After U-bending (cold forming), heat treatment of the bent part may be necessary. Pantani Divisione Tubi is equipped with 2 heat treatment machines and 1 nitrogen generator (to protect the surface of the stainless steel tubes during annealing). The temperature is controlled throughout the heat-treated area by fixed and portable infrared pyrometers.
| Tube OD | Tube thickness | Bending Radius | Straight “leg” length | Straight tube before U bending |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min. 12,7 mm / Max. 31,75 mm | Min. 0,70 mm / Max. 4,19 mm | Min. 1,5 x OD / Max. 1.250 mm |
Max. 12.500 mm | Max. 27.000 mm |


Standards usually required to establish U bend tube tolerances:
The semi-finished product for U bend tubes are heat exchanger tubes, manufactured and supplied according to DIN 28180 and ASTM A179.
Tubes for heat exchangers are made of steel according to:
| Standard | Application |
|---|---|
| ASTM A179 | Seamless Cold-Drawn Low-Carbon Steel Heat-Exchanger and Condenser Tubes |
| ASTM A192 | Seamless Carbon Steel Boiler Tubes for High-Pressure Service |
| ASTM A210 | Seamless Medium-Carbon Steel Boiler and Superheater Tubes |
| ASTM A213 | seamless Ferritic and Austenitic Alloy-Steel Boiler, Superheater, and Heat-Exchanger Tubes |
| ASTM A334 | Seamless Steel Pipe for Low-Temperature Service and other Applications with Required Notch Toughness |
| JIS G3461/2 | carbon steel tubes used for heat exchange in boilers, heat exchangers, condensers, and similar equipment |
| EN10216-1/2 | specified the standard of cold processed precision steel tubes in a wide range of sizes |
| DIN17175 | seamless tubes for high-pressure and high-temperature applications, specifically for boilers and heat exchangers |
| Standard | Grade | Chemical Components (%) | Mechanical Properties | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Mo | Cr | V | T.S. (Mpa) | Y.S. (Mpa) | E.L. (%) | Hardness (HRB) | ||
| ASME SA179 | SA179 | 0.06-0.18 | / | 0.27-0.63 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.035 | / | / | / | ≥325 | ≥180 | ≥35 | ≤72 |
| ASME SA192 | SA192 | 0.06-0.18 | ≤0.25 | 0.27-0.63 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.035 | / | / | / | ≥325 | ≥180 | ≥35 | ≤77 | ASME SA210 | A1 | ≤0.27 | ≥0.10 | ≤0.93 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.035 | / | / | / | ≥415 | ≥255 | ≥30 | ≤79 |
| C | ≤0.35 | ≥0.10 | 0.29-1.06 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.035 | / | / | / | ≥485 | ≥275 | ≥30 | ≤89 | |
| ASTM A333 /A334 | GR.1 | ≤0.30 | / | 0.4-1.06 | ≤0.025 | ≤0.025 | / | / | / | ≥380 | ≥205 | ≥35 | -45° |
| GR.6 | ≤0.30 | ≥0.10 | 0.29-1.06 | ≤0.025 | ≤0.025 | / | / | / | ≥415 | ≥240 | ≥30 | -45° | |
| GR.8 | ≤0.13 | 0.13-0.32 | ≤0.90 | ≤0.025 | ≤0.025 | / | / | 8.40-9.60 | ≥690 | ≥515 | ≥22 | -195° | |
U bend tubes for heat exchangers applied mostly in oil and gas plants, chemical and petrochemical plants, refineries, power plants and renewable energy plants. Low fin tubes can be supplied in the form of U bends.
U-bend tubes are widely used in heat-exchanger systems. Heat-exchanger equipment on the basis of seamless stainless U-tubes is essential in strategically important and critical fields — nuclear and petrochemical machine building.
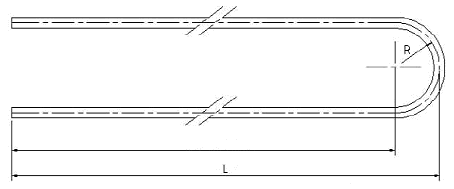
| Item | Condition (when) | Tolerance |
|---|---|---|
| Ovality | Nominal bend radius ≤ 2 x nominal OD | less than or equal to 12% |
| 2 x nominal OD < Nominal bend radius ≤ 4 x nominal OD | less than or equal to 10% | |
| Nominal bend radius > 4 x nominal OD | less than or equal to 5% | |
| Nominal bend radius ≤ 2 x nominal OD | 0.75 x nominal wall | |
| Mimimum wall thickness | 2 x nominal OD < Nominal bend radius ≤ 4 x nominal OD | 0.8 x nominal wall |
| Nominal bend radius > 4 x nominal OD | 0.9 x nominal wall | |
| Nominal bend radius ≤ 8" (200mm) | +/-3/64"(1mm) | |
| Bending Radius | 8" (200mm) < Nominal bend radius ≤ 16" (400mm) | +/-1/16"(1mm) |
| Nominal bend radius >16" (400mm) | +/-5/64"(1mm) | |
| Disrance between legs | Max 1/16"(1.5mm) | |
| Wall thinning of bending area | Max 17% | |
| Difference between leg lengths at the ends | Leg length ≤ 16' (4.88m) | +1/8"(3mm) |
| Leg length > 16' (4.88m) | +3/16"(5mm) | |
| Deviation from plane of bend | ≤ 3/16"(1.5mm) | |
| Flattening on bend | ≤ 10% nominal diameter | |
| Straight leg length | ≤5m | +1/8"(3mm) |
| >5m | +3/16(5mm) | |
| Total tube length including radius | ≤6m | +3/16(5mm) |
| >6m | +5/16"(8mm) |
U-Tube heat exchangers are known for their distinctive U-shaped tubes that offer several advantages and also come with certain limitations.
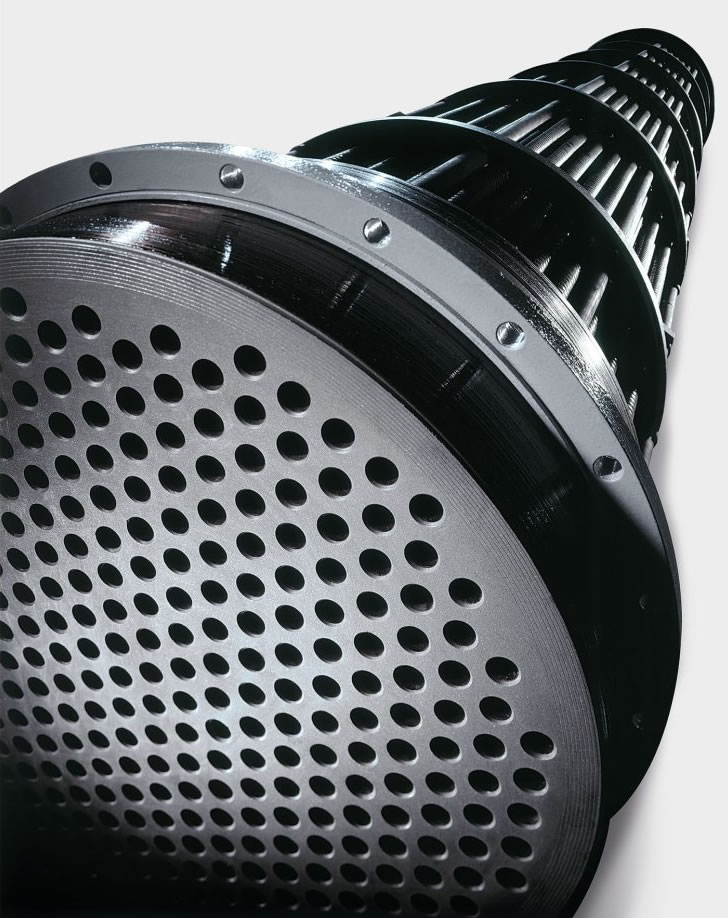
The U-tube heat exchanger features a single tubesheet with both ends of the tubes secured to it. This design allows the tubes to expand and contract freely, avoiding thermal stress and offering excellent thermal compensation. A double tube pass is utilized, providing a lengthy process path, high flow rates, and superior heat transfer performance with robust pressure resistance. The tube bundle is removable from the shell for convenient maintenance and cleaning, presenting a simple structure and low cost.
Limitations imposed by the elbow's curvature radius restrict the arrangement of heat exchange tubes. This results in a larger inner tube spacing within the tube bundle and a lower utilization rate of the tube sheet. The shell-side fluid is prone to short-circuiting, which can impede heat transfer. When a tube leaks or sustains damage, only the U-shaped tubes on the outer part of the bundle can be readily replaced. Damage to the inner heat exchange tubes is not as easily repairable and may require blocking off. Furthermore, the damage to a single U-shaped tube equates to the loss of two tubes, leading to a higher scrap rate.
‘U’ bends are produced, controlled and measured fully in accordance with relevant standards.
U-bend tubes, also known as U-bent tubes or U-shaped tubes, are typically made from a variety of materials depending on the specific application and industry requirements. The choice of material for U-bend tubes is crucial because it impacts factors such as corrosion resistance, heat resistance, and overall durability. Common materials used for U-bend tubes include:
| Material | Grade |
|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | SA 179 / A 179 |
| Carbon Steel | SA 210 / A 210 |
| Carbon Steel | SA 334 / A 334 |
| Stainless Steel | SA 213 / A 213 |
| Duplex Stainless Steel | SA 789 / A 789 |
| Copper & Cu Alloys | SB 111 / B 111 |
| Titanium & Ti Alloys | SB 338 / B 338 |
For different materials please contact our sales department.
Carbon Steel: Carbon steel U-bend tubes are cost-effective and suitable for applications where corrosion resistance is not a primary concern. They are commonly used in low to moderate-temperature systems.
Stainless Steel: Stainless steel U-bend tubes are known for their excellent corrosion resistance, making them suitable for applications where exposure to corrosive environments or high temperatures is a concern. Different grades of stainless steel, such as 304, 316, and 321, can be used depending on the specific requirements.
Copper and Copper Alloys: Copper U-bend tubes are excellent conductors of heat and electricity. They are often used in applications like HVAC systems and refrigeration due to their high thermal conductivity.
Aluminum: Aluminum U-bend tubes are lightweight and have good thermal conductivity. They are used in various heat exchange applications, including automotive radiators and air conditioning systems.
Inconel: Inconel U-bend tubes are known for their high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for applications in extreme environments, such as aerospace and chemical processing.
Titanium: Titanium U-bend tubes offer exceptional corrosion resistance, especially in highly corrosive environments. They are used in industries like chemical processing and marine applications.
The material selection for U-bend tubes depends on factors like temperature, pressure, the nature of the fluid or gas being transported, and the specific requirements of the system. It's essential to choose the right material to ensure the longevity and performance of the U-bend tube in its intended application.
Finned tube coils are heat exchangers that consist of a series of tubes to which fins are attached.







Cast basalt is the most frequently used wear protection material.
Equipment used for mining and industry which includes hydraulic and pneumatic piping systems for wet and dry material transfer such as fly ash, ash sluice pits, pulverised coal, coal slurry and many other abrasive transport uses.
The main areas of application are the wear resistant linings for: Piping. Mechanical conveyor systems such as chutes, trenches, and chain conveyors.
The key differences between tubes and pipes are centered around their use and how they are measured:
For structural integrity, the OD and wall thickness of tubing are essential. Tubes can also come in square or rectangular shapes, not just round. Pipes are identified by their Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) in inches or "diameter nominal" (DN) in the metric system, which is based on the ID and is a standard dimension.
Our customized U-bend tubes are meticulously crafted to meet your specific requirements and applications. These tubes are engineered with precision to ensure optimal performance and reliability in various heat exchange systems.






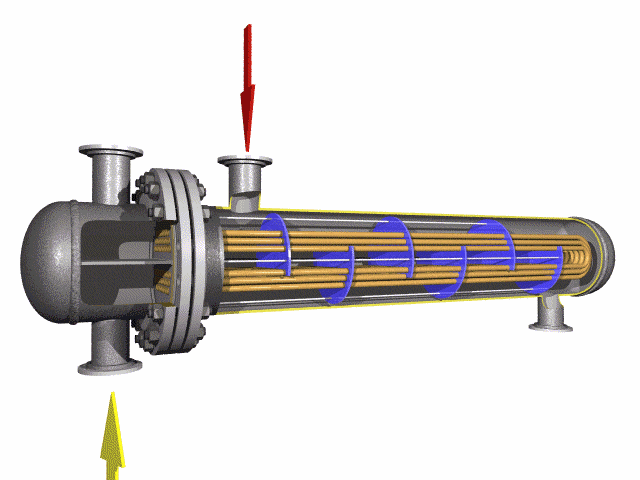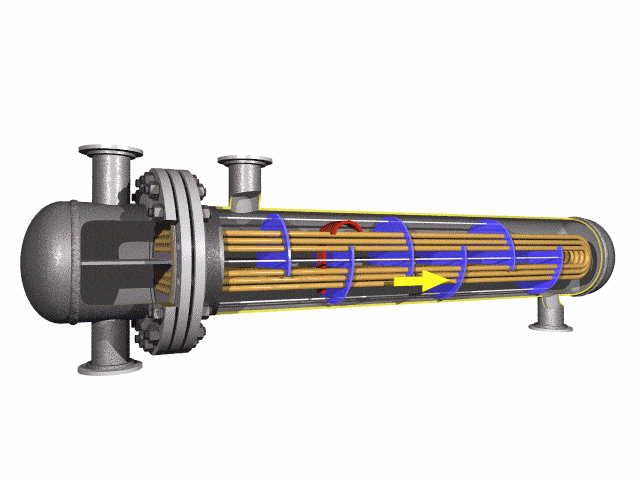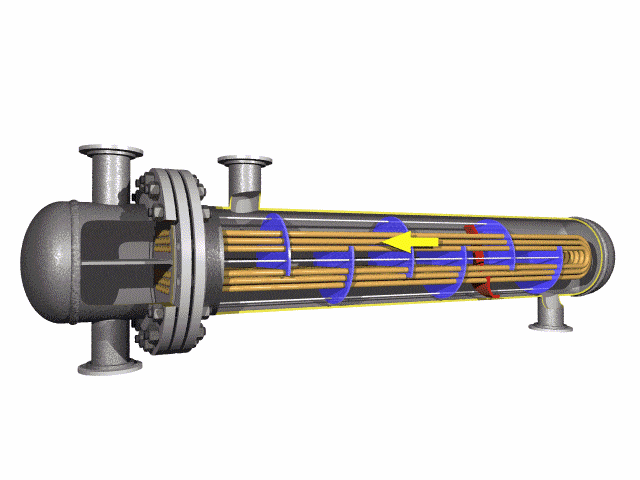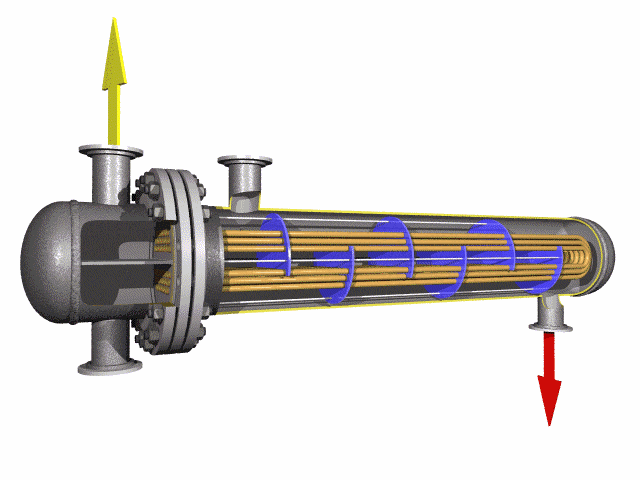
U-bend tubes are used to transfer heat between fluids. They can return the flow of coolants/fluids at 180 degrees in a much smaller space.
The common application fields are: heat exchangers (condensers, evaporators, sea water desalinators) chemical and petrochemical industries. food processing and refrigeration industries.
Heat-exchanger equipment on the basis of seamless stainless U-tubes is essential in strategically important and critical fields — nuclear and petrochemical machine building.
Fin tubes are used in applications involving the transfer of heat from a hot fluid to a colder fluid through a tube wall. Furthermore, finned tubes are used when the heat transfer coefficient on the outside of the tubes is appreciably lower than that on the inside.
As the pipes warm up they expand, the bend allows this expansion to proceed without buckling the pipes. Alternatively, flexible or sliding types of expansion provision are available, and large pipes are mounted on rollers.
We packs all U Tube bundles in bespoke wooden boxes and separate all U Tubes of different radii using finger pallets to facilitate easy assembly of bundles on receipt.
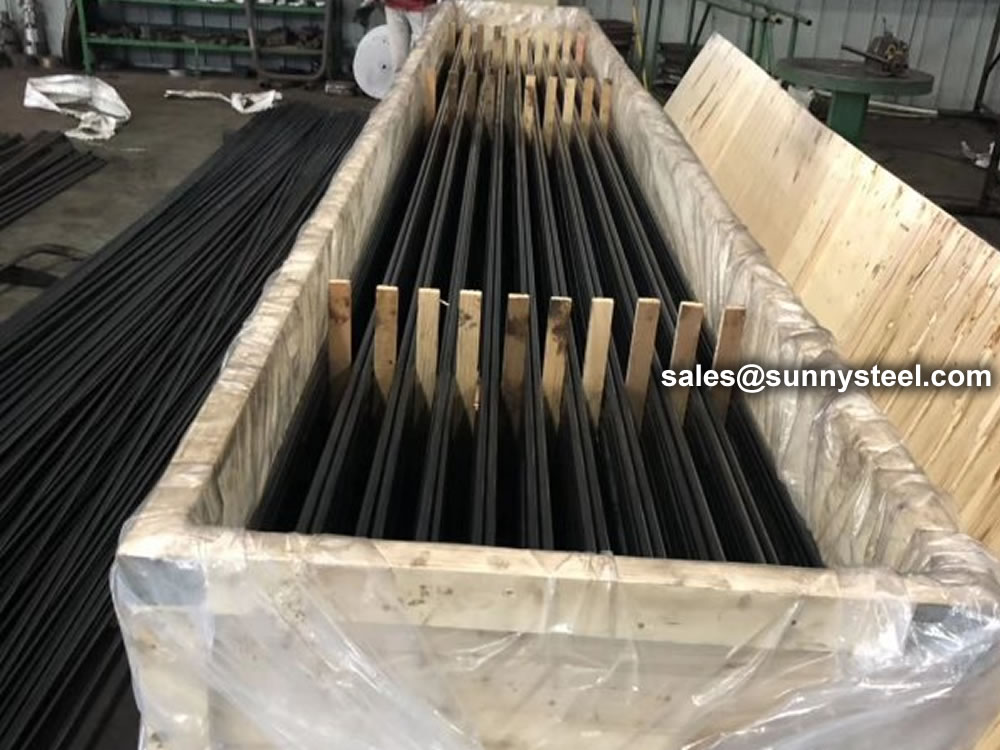
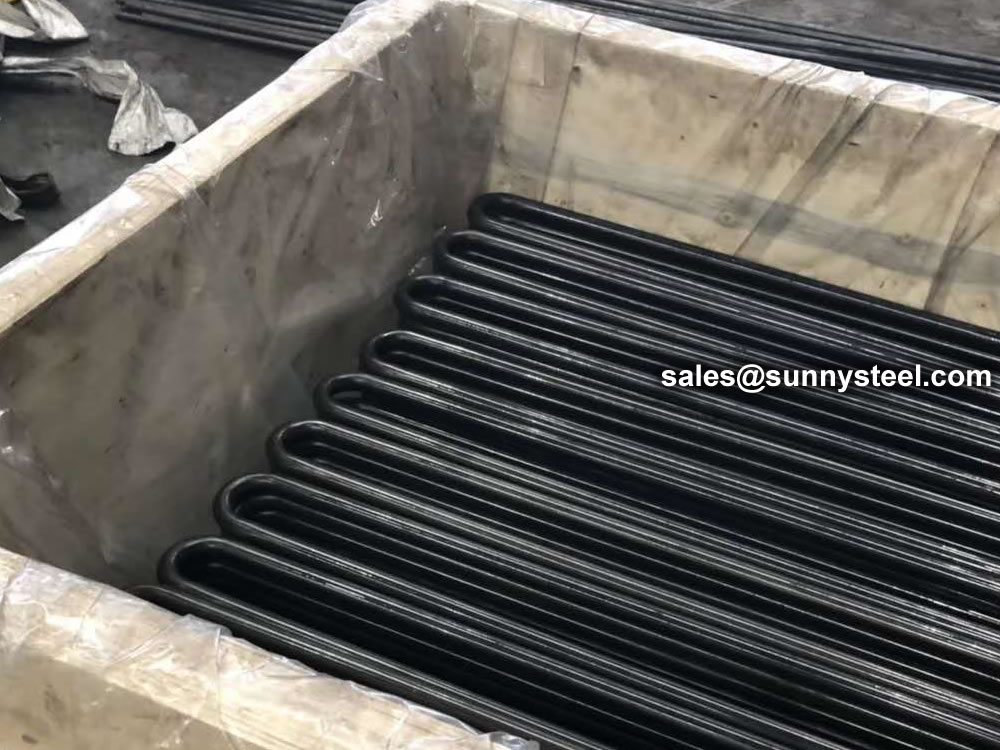
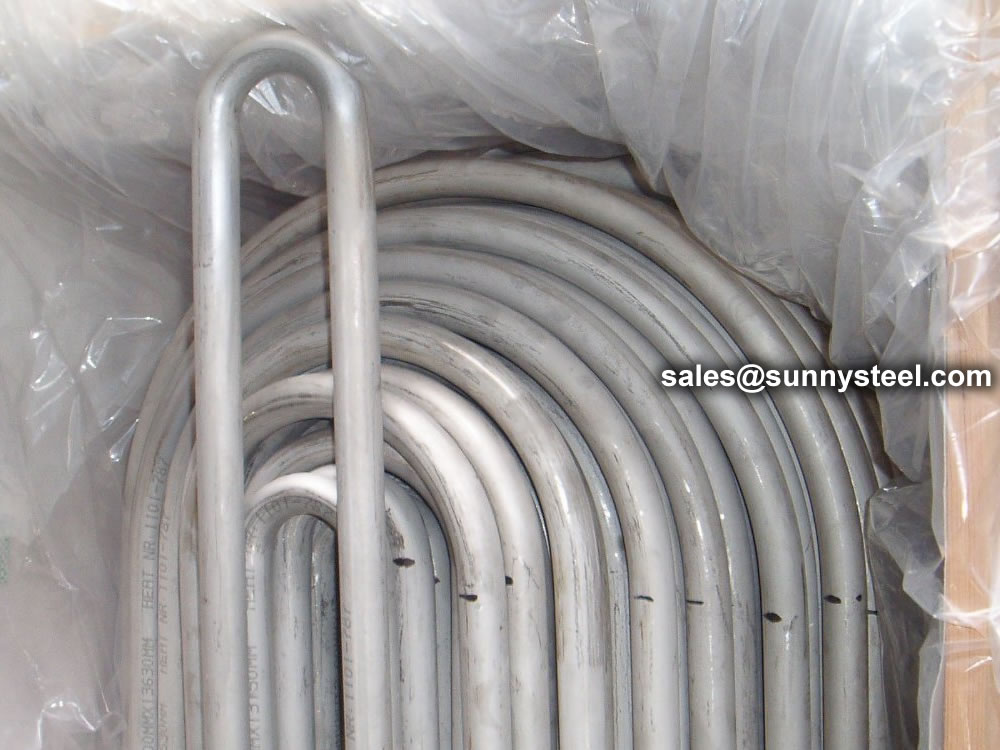
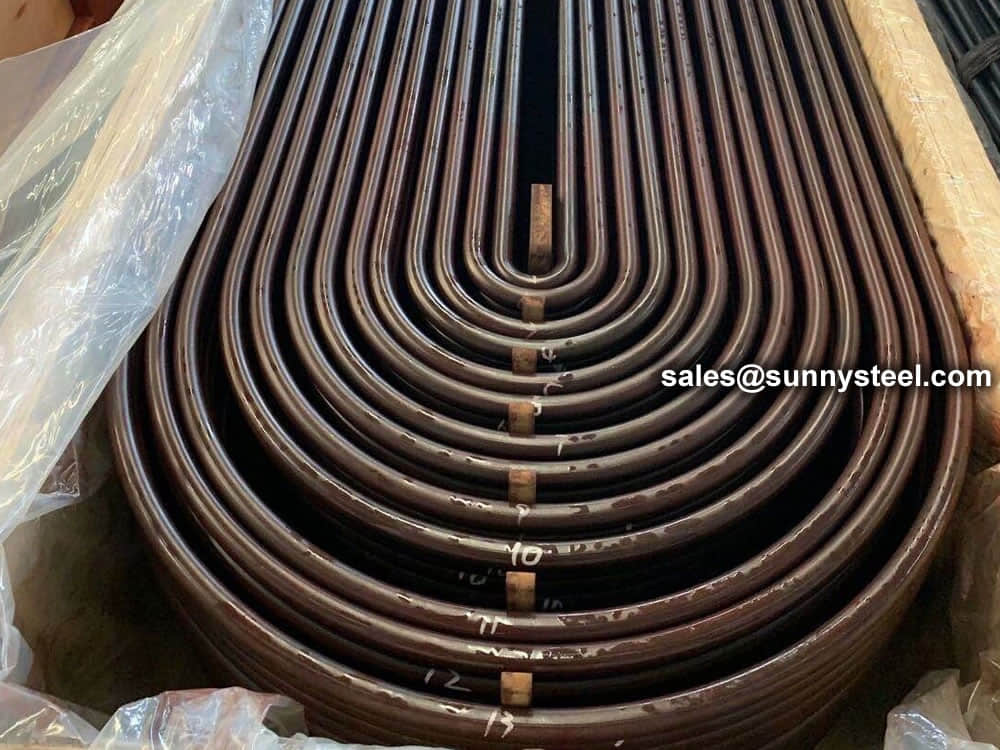
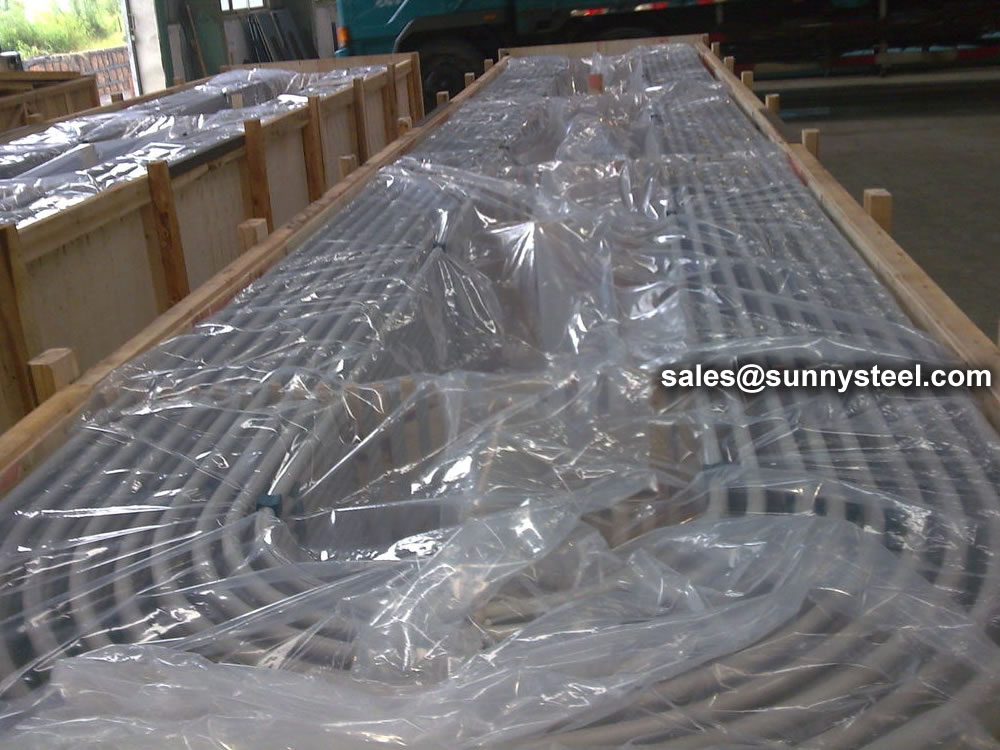






Any type of packing is available according to customer need to worldwide destinations.


