Bearing Pipes
Pipes designed for bearing loads, offering high strength and durability.


DIN/EN steel pipes refer to steel pipes that adhere to the standards set by the Deutsches Institut für Normung (DIN) and European Norm (EN).
DIN represents German interests in international organizations such as CEN, the European standards body, and ISO, the International Standards Organization. Today, roughly 85 % of all national standards projects are European or international in origin.
DIN/EN steel pipes are used in various applications across industries such as construction, oil and gas, automotive, and manufacturing. They are suitable for conveying fluids, gases, and solids, as well as for structural purposes. DIN/EN standards specify the dimensions and tolerances for steel pipes. These include parameters such as outer diameter, wall thickness, length, and straightness. Compliance with these standards ensures uniformity and interchangeability of steel pipes.
EN10216-2 P235GH TC1 seamless alloy steel pipes are primarily used for high-temperature and high-pressure applications, such as power generation, boiler systems, and heat exchangers.
P235GH TC1 seamless boiler tubes are high-quality, heat-resistant tubes used in the construction of boilers and heat exchangers. These tubes are made from P235GH TC1 steel, which is a European standard carbon steel designed for elevated temperature service.
Here are some key points about P235GH TC1 seamless boiler tubes:
The specific chemical composition of EN10216-2 P235GH TC1 steel is not provided in the search results. However, it is mentioned that P235GH is a carbon steel material with good cold working and hot working characteristics, making it suitable for pipes transporting hot liquids.

With so many European Standards specifying steel and steel products and replacing national standards, it is necessary to have a European designation system for steel.
Such a system is well established and implemented in almost all the European Standards. European Standards for steel products are the responsibility of the European Committee for Iron and Steel Standardization.
ECISS has the task of developing European Standards for the definition, classification, testing, analysis and technical delivery requirements for the products of the iron and steel industry and the implementation of these as national standards by members in order to achieve technical harmonization within the European Union. ECISS is an Associated Standards Body within the framework of the European Committee of Standardization.
European Standards published in the UK have the status of a British Standard and are characterized by the prefix ‘BS EN’ to their reference number. Other national standards bodies of Member States of the European Union publish identical European Standards with their appropriate prefixes, e.g. in Germany, ‘DIN EN’, in France ‘NF EN’, in Sweden ‘SIS EN’ etc. European Standards are essentially voluntary instruments except for certain situations, e.g. Public Procurement Directives, Construction Products Directive. According to the CEN rules, members in the UK, that is BSI, are obliged to announce the availability of European Standards and publish the identical text and to withdraw any conflicting national standards.
BS 3059-2:1990 requirements for tubes not exceeding 127 mm outside diameter and 12.5 mm thickness. Depending on the operating temperature, it can be divided into two kinds general boiler pipes and high-pressure boiler pipes.
BS 3059 PART 2-78 is the standard specifies the steel boiler and superheter tubes carbonn alloy and specified elevated temperature prop.
P235GH is a European specified steel for use in pressure vessels, boilers and heat exchangers. The composition of this steel makes it ideal for applications where elevated working temperatures are the norm and the material is used by fabricators throughout the oil, gas and petrochemical industry.
Seamless steel tubes for pressure purposes
Material
DIN 17175 steel pipes are used in boiler installations, high-pressure pipelines and tank construction and special machinery for both high (градусов 600) temperature and high-pressure devices. This alloy steel pipe is just a big class,and it has many classifivations.
P265GH is a weldable pressure vessel and boiler steel grade used by the world’s industrial fabricators. The material, which is ideally suited for elevated temperature service, is commonly found in the oil & gas, petrochemical and chemical industry.
DIN 2391 standard specifies the Seamless steel tubes used forMechanical and Automobile.
The British Standard Pipe (BSP) is a family of standard screw thread types that has been adopted internationally for interconnecting and sealing pipe ends by mating an external (male) with an internal (female) thread.
BS 3059 standard accord to the steel boiler and superheater tubes. Part I-87 low tensile carbon steel tube without specified elevated temperature preperites.
The DIN 2440 standard applies to medium-weight tubes suitable for screwing used in applications of medium pressure air and non-hazardous gases. The most common material is St33.2(also known as S185) conforming to DIN 17100. DIN 2440 steel pipes are often supplied in seamless type with zinc coating.
Over the years, many DIN standards were integrated into the ISO standards, and thus also a part of the EN standards. In the cource of the revision of the European standards serveral DIN standards were withdrawn and replaced by DIN ISO EN and DIN EN.
The standards used in the past such as the DIN 17121, DIN 1629, DIN 2448 and the DIN 17175 have since been mostly replaced by Euronorms. The Euronorms clearly distinguish the pipe's area of application. Consequently different standards now exist for pipes used as construction materials, pipelines or for mechanical engineering applications.
This distinction was not as clear in the past. For example, the old St.52.0 quality was derived from the DIN 1629 standard which was intended for pipeline systems and mechanical engineering applications. This quality was also often used for steel structures, however.
The info below explains the main standards and steel qualities under the new system of standards.
The EN 10216 Euronorm replaces the old DIN 17175 and 1629 standards. This standard is designed for pipes used in pressure applications, such as a pipeline. This is why the associated steel qualities are designated by the letter P for 'Pressure'. The value that follows this letter designates the minimum yield strength. The subsequent letter designations provide additional information.
The EN 10216 comprises several parts. The parts that are relevant to us are as follows:
Some examples:
* Normalized is defined as: normalized (warm) rolled or standard annealing (at a min temperature of 930°C). This applies to allqualities designated by the letter 'N' in the new Euro Standards.
Pipes: the following standards are replaced by DIN EN
Old standard
| Execution | Norm | Steel grade |
| Welded | DIN 1626 | St.37.0 |
| Welded | DIN 1626 | St.52.2 |
| Seamless | DIN 1629 | St.37.0 |
| Seamless | DIN 1629 | St.52.2 |
| Seamless | DIN 17175 | St.35.8/1 |
| Seamless | ASTM A106* | Grade B |
| Seamless | ASTM A333* | Grade 6 |
New standard
| Execution | Norm | Steel grade |
| Welded | DIN EN 10217-1 | P235TR2 |
| Welded | DIN EN 10217-3 | P355N |
| Seamless | DIN EN 10216-1 | P235TR2 |
| Seamless | DIN EN 10216-3 | P355N |
| Seamless | DIN EN 10216-2 | P235GH |
| Seamless | DIN EN 10216-2 | P265GH |
| Seamless | DIN EN 10216-4 | P265NL |
* ASTM standards will remain valid and will not be replaced by Euronorms in the near future
Gain an insight into the difference between DIN, EN and ISO standards!
Here you can find information on what changes have been made to the respective product standard and what differences between the DIN, EN and ISO standards this has caused. Get an overview and use the clear direct comparison of the withdrawn DIN standards and the current EN and ISO standards.
In the past, standardisation work in Germany was carried out on a national level by Deutsches Institut für Normung e. V. (DIN). On a European level there are also EN standards, as well as ISO standards on an international level, which are issued by the International Organization for Standardization.

The differences
National standards (DIN) are largely being replaced by international and European standards. DIN standards are now only issued for products that have no ISO or EN standards
In accordance with the task and objective of the ISO, which was founded in 1946, international standards (ISO) are intended to standardise technical rules worldwide, thus simplifying the exchange of goods and removing trade barriers.
The purpose of European standards (EN) is to harmonise technical rules and laws within the single European market that was jointly established on 01/01/1993. As far as possible, existing ISO standards must generally be adopted as EN standards in unaltered form. The difference between ISO and EN standards is that, following the decision of the European Council, EN standards must be adopted and implemented immediately and without any changes as national standards in the member states, and, at the same time, the corresponding national standards must be withdrawn.
With years of expertise, we provide a diverse array of steel tube processing options. From sawing and machining tube blanks to intricate bending and upsetting operations, we actively assist you throughout your projects.
Our capabilities extend to eccentricity reduction and concentricity enhancement through turning and grinding. We excel in creating complex geometries using processes like rotary swaging and axial forming. Additionally, we offer property modifications via partial heat treatment, ensuring tailored solutions for your specific needs.











Seamless steel pipe is regularly used in the transportation of fluids such as water, natural gas, waste and air. It is also regularly required in many high-pressure, high-corrosive environments such as in the oil & gas, power generation and pharmaceutical industries. Some common uses of seamless pipes include:
DIN steel heat exchanger tubes, meeting German Industrial Standards, are constructed from high-temperature and corrosion-resistant steel, specifically designed for efficient heat exchange applications.
Steel pipe delivery status(condition): cold / hard (BK), cold / soft (BKW), after cold stress relief annealing (BKS), annealing (GBK), normalized (NBK).
| Term | Symbol | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Cold-finished/hard (cold-finished as-drawn) | BK | No heat treatment after the last cold-forming process. The tubes therefore have only low deformability. |
| Cold-finished/soft (lightly cold-worked) | BKW | After the last heat treatment there is a light finishing pass (cold drawing) With proper subsequent processing, the tube can be cold-formed (e.g. bent, expanded) within certain limits. |
| Annealed | GBK | After the final cold-forming process the tubes are annealed in a controlled atmosphere or under vacuum. |
| Normalized | NBK | The tubes are annealed above the upper transformation point in a controlled atmosphere or under vacuum. |
The general cold strip mills, volume should go through continuous annealing (CAPL unit) to eliminate cold hardening and rolling stress, or batch annealing reach the mechanical properties of the corresponding standard specifies. Cold rolled steel surface quality, appearance, dimensional accuracy better than hot-rolled plate, and right-rolled thin product thickness is about 0.18mm, so the majority of users favor.
Cold rolled steel coil substrate products deep processing of high value-added products. Such as electro-galvanized, hot dip galvanized, electro-galvanized fingerprint resistant, painted steel roll damping composite steel, PVC laminating steel plates, etc., so that the excellent quality of these products has a beautiful, high resistance to corrosion, has been widely used.
Cold rolled steel coil finishing after annealing, cut the head, tail, trimming, flattening, smooth, heavy volume, or longitudinal clipboard. Cold-rolled products are widely used in automobile manufacturing, household electrical appliances, instruments, switches, buildings, office furniture and other industries. Steel plate strapping package weight of 3 to 5 tons. Flat sub-volume typically 3 to 10 tons / volume. Coil diameter 6m.
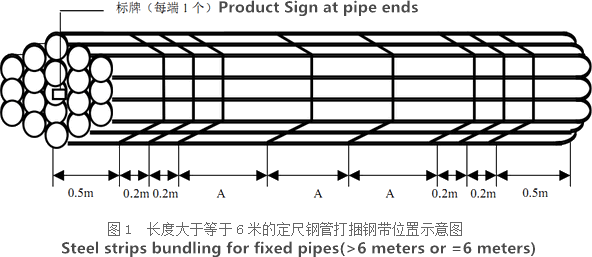
Bare packing/bundle packing/crate packing/wooden protection at the both sides of tubes and suitably protected for sea-worthly delivery or as requested.
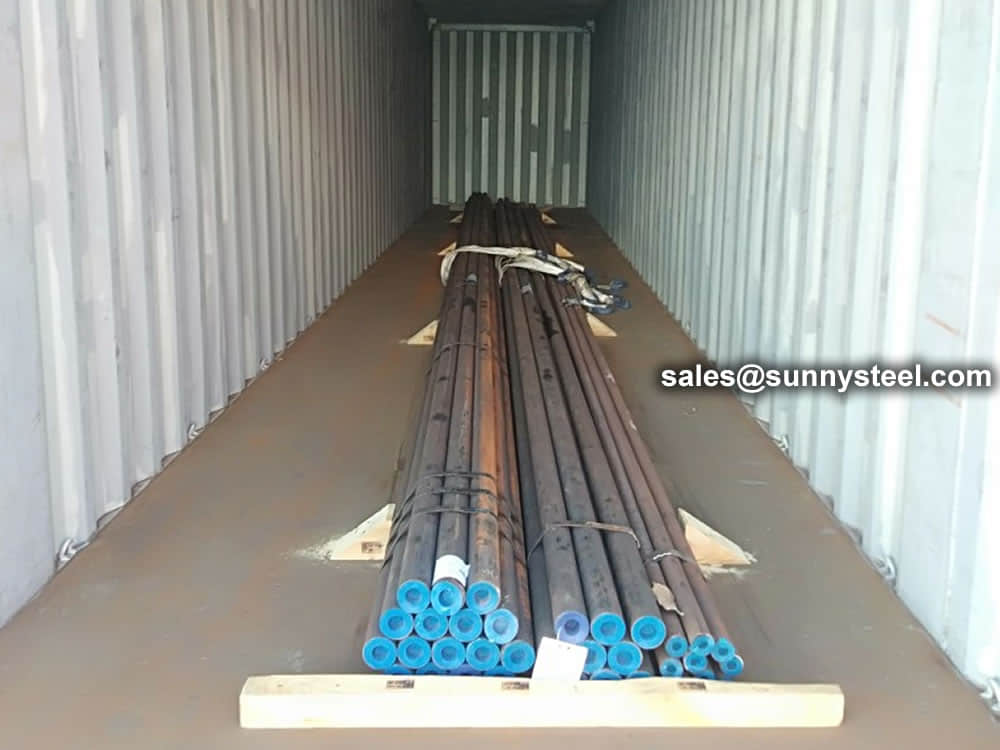
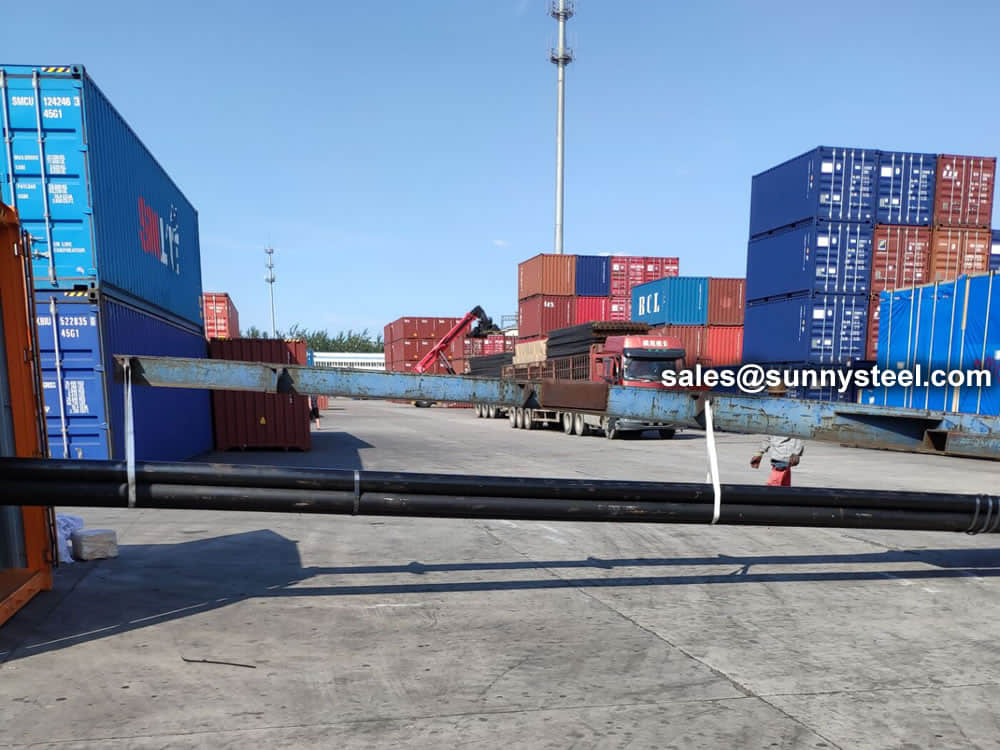
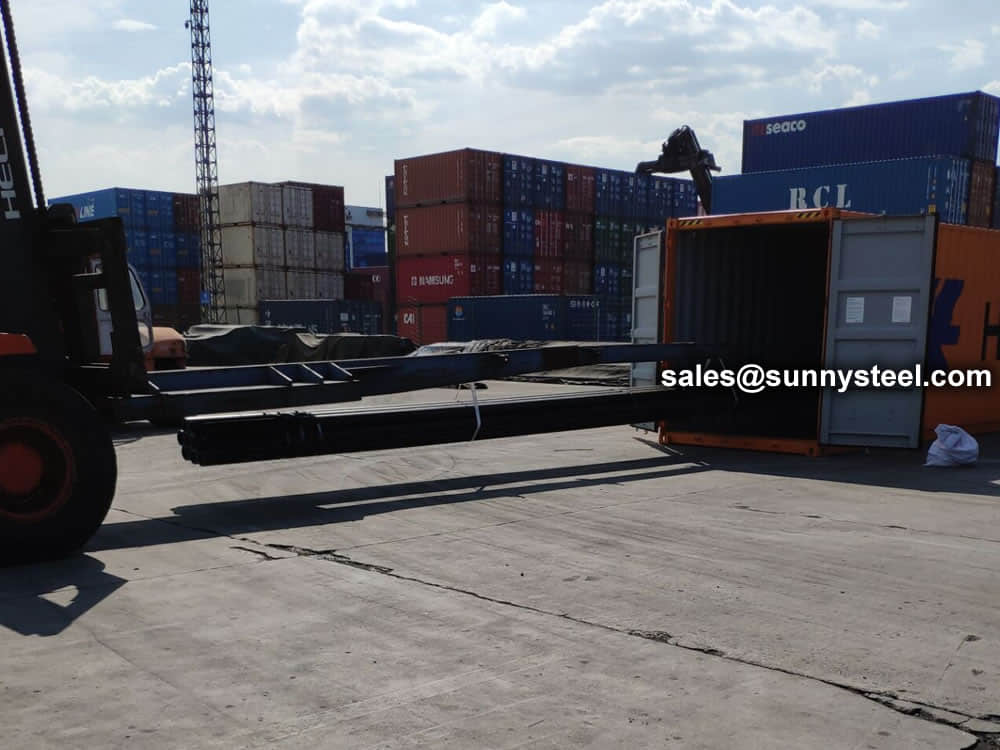
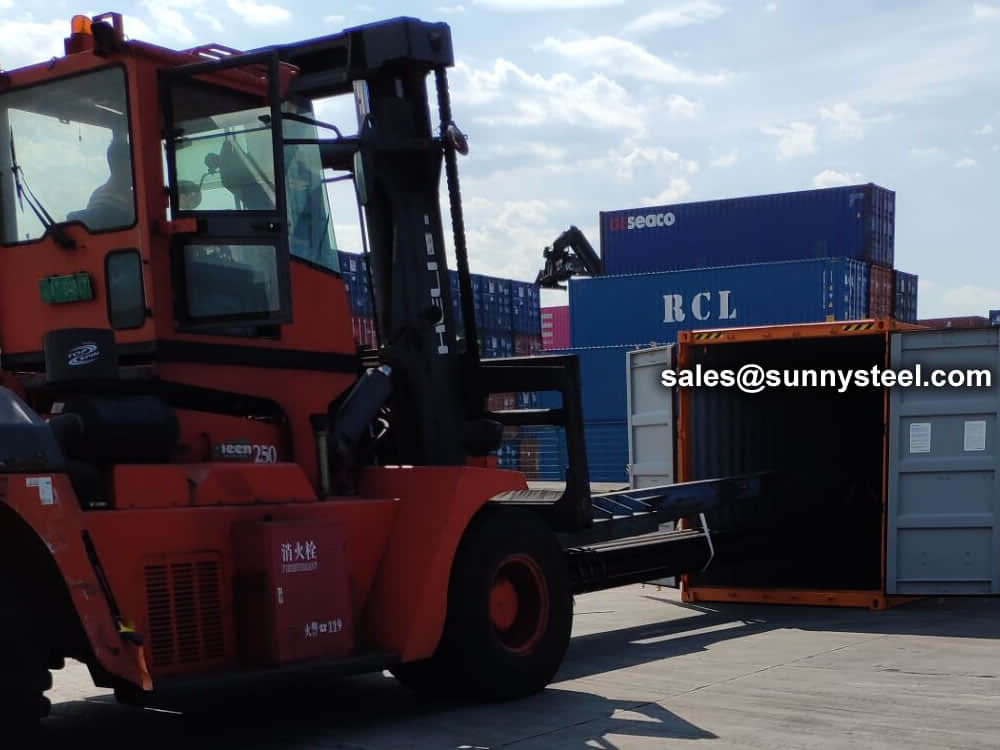
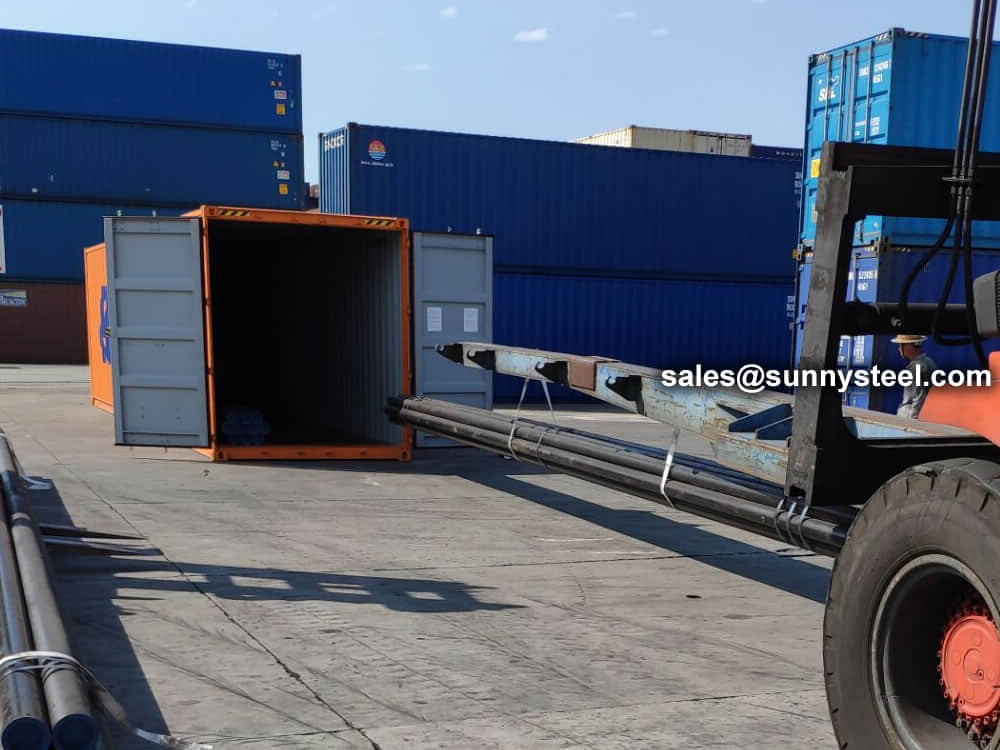
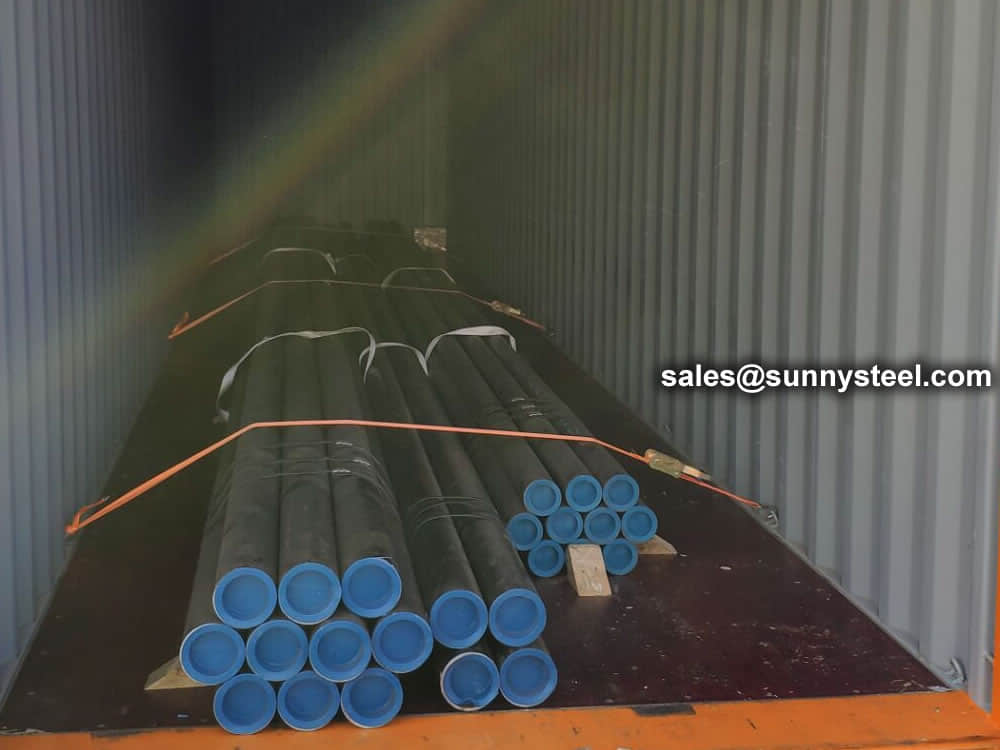
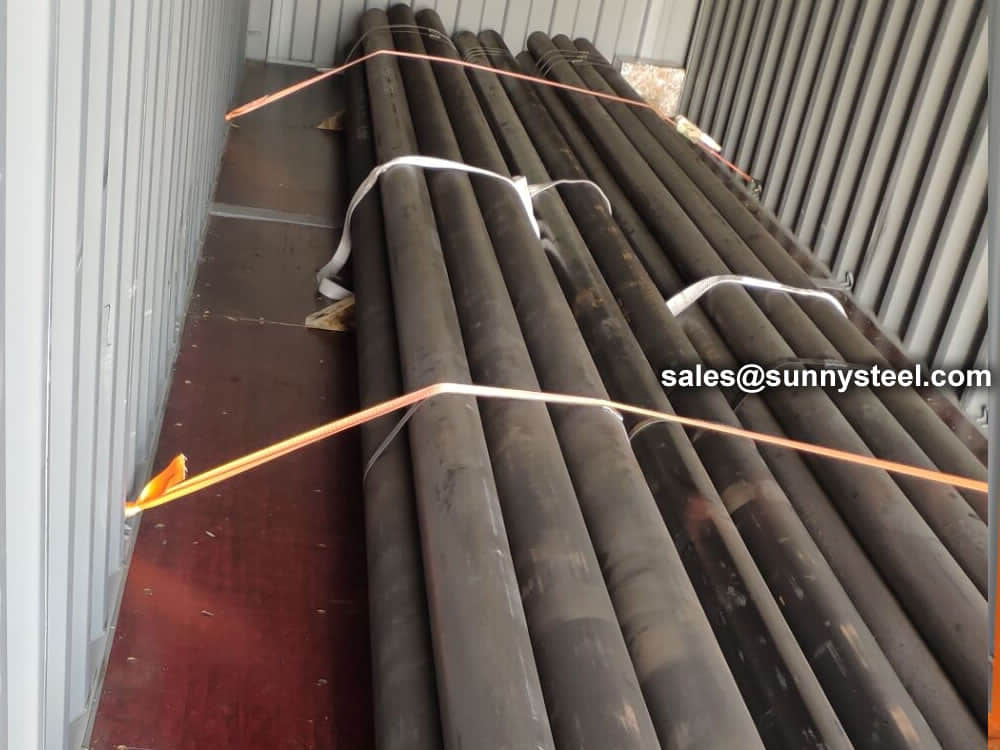












There are probably hundreds of different methods for packing a pipe, and most of them have merit, but there are two principles that are vital for any method to work prevent rusting and Sea transportation security.
Our packing can meet any needs of the customers.
Commonly used alloying elements and their effects are listed in the table given below.
| Alloying Elements | Effect on the Properties |
|---|---|
| Chromium | Increases Resistance to corrosion and oxidation. Increases hardenability and wear resistance. Increases high temperature strength. |
| Nickel | Increases hardenability. Improves toughness. Increases impact strength at low temperatures. |
| Molybdenum | Increases hardenability, high temperature hardness, and wear resistance. Enhances the effects of other alloying elements. Eliminate temper brittleness in steels. Increases high temperature strength. |
| Manganese | Increases hardenability. Combines with sulfur to reduce its adverse effects. |
| Vanadium | Increases hardenability, high temperature hardness, and wear resistance. Improves fatigue resistance. |
| Titanium | Strongest carbide former. Added to stainless steel to prevent precipitation of chromium carbide. |
| Silicon | Removes oxygen in steel making. Improves toughness. Increases hardness ability |
| Boron | Increases hardenability. Produces fine grain size. |
| Aluminum | Forms nitride in nitriding steels. Produces fine grain size in casting. Removes oxygen in steel melting. |
| Cobalt | Increases heat and wear resistance. |
| Tungsten | Increases hardness at elevated temperatures. Refines grain size. |
