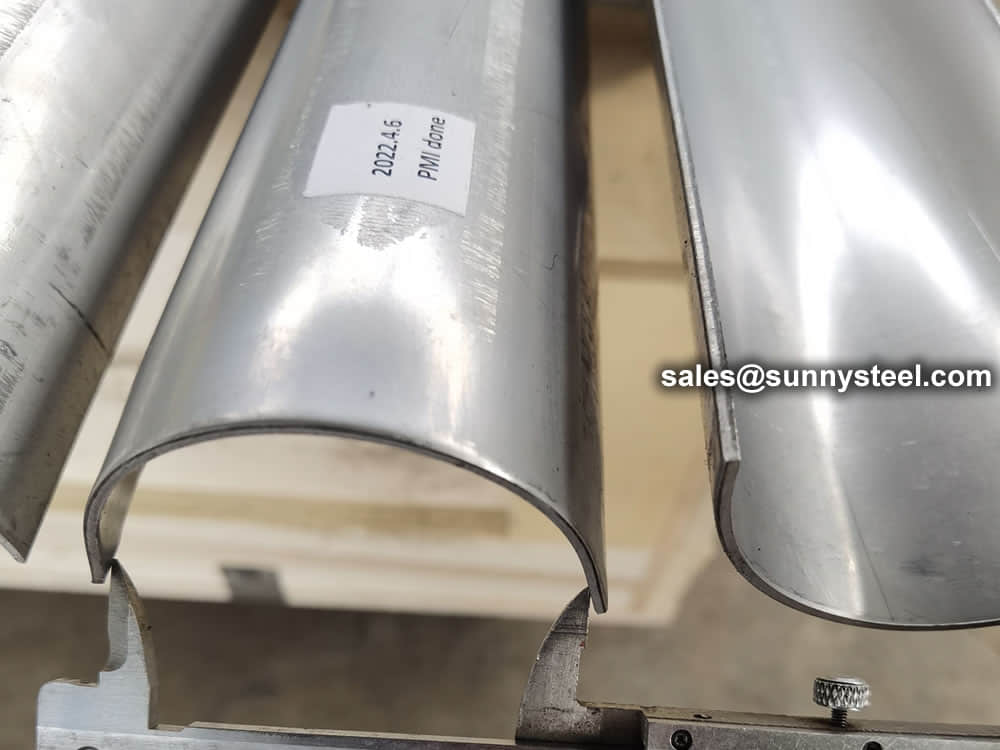

Gas fired stainless steel tube boiler climbing pipe erosion shield is a common component of the heating part of tubes.
Download PDFClimbing Pipe Erosion Shields are essential for protecting the climbing pipes in gas fired stainless steel tube boilers from high-temperature erosion, wear, and corrosion. These shields are designed to extend the life of the pipes and reduce maintenance costs associated with pipe failure.
Common materials for climbing pipe erosion shields include:
Climbing Pipe Erosion Shields are primarily used in gas fired stainless steel tube boilers where high temperatures and pressures can cause accelerated erosion and wear on the climbing pipes. These shields provide a protective barrier against these harsh conditions.
The service life of climbing pipe erosion shields can vary depending on the specific application and operating conditions. Regular inspection and maintenance are recommended to ensure the continued effectiveness of the shields and to identify any signs of wear or damage that may require replacement.
Investing in climbing pipe erosion shields for gas fired stainless steel tube boilers is a strategic decision that can lead to significant economic benefits and improved system reliability. By protecting the pipes from erosion and wear, these shields help to minimize maintenance costs and extend the service life of the boiler.
The useful life of tube shield is 3-5years. The tube shield has a variety of material and the selection of the material shall be subject to the original design of the boiler.The tube shield is divided into straight pipe and bend pipe.
The main effect of tube shield is to protect the pipe and increase the service life of the pipe. Boiler tube shields are designed to eliminate major maintenance and downtime costs from boiler and condenser tube failure.
| Material | Standard | Material |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | ASTM | 201, 202, 301, 304, 304L, 304N, XM21, 304LN, 305, 309S, 310S, 316, 316Ti, 316L, 316N, 316LN, 317, 317L, 321, 347, 329, 405, 409, 430, 434, 444, 403, 410, 420, 440A, etc. |
| EN | 1.4372, 1.4373, 1.4319, 1.4301, 1.4306, 1.4315, 1.4303, 1.4833, 1.4845, 1.4401, 1.4571, 1.4404, 1.4429, 1.4438, 1.4541, 1.4550, 1.4477, 1.4462, 1.4002, 1.4512, 1.4016, 1.4113, 1.4509, 1.4521, 1.4006, 1.4021, 1.4028, etc. | |
| JIS | SUS201, SUS202, SUS301, SUS304, SUS304L, SUS304N1, SUS304N2, SUS304LN, SUS305, SUS309S, SUS310S, SUS316, SUS316L, SUS316TI, SUS316N, SUS316LN, SUS316J1, SUS316J1L, SUS317, SUS317L, SUS321, SUS347, SUS329J1, SUS329J3L, SUS405, SUH409, SUS410L, SUS430, SUS434, SUS444, SUS403, SUS410, SUS420J1, SUS420J2, SUS440A, SUS440B, SUS440C, etc. |
The cross-sectional shape of boiler tubes shields is mostly semi-circular (180 degrees), and there are also 120-160 degrees.
It is mainly used on finned tubes (water-cooled walls); boiler tube erosion shields are divided into direct wear-resistant shields, in-curve, anti-wear shields, outer-curve, anti-wear shields, side-curve anti-wear shields, s-curve anti-wear shields, etc.
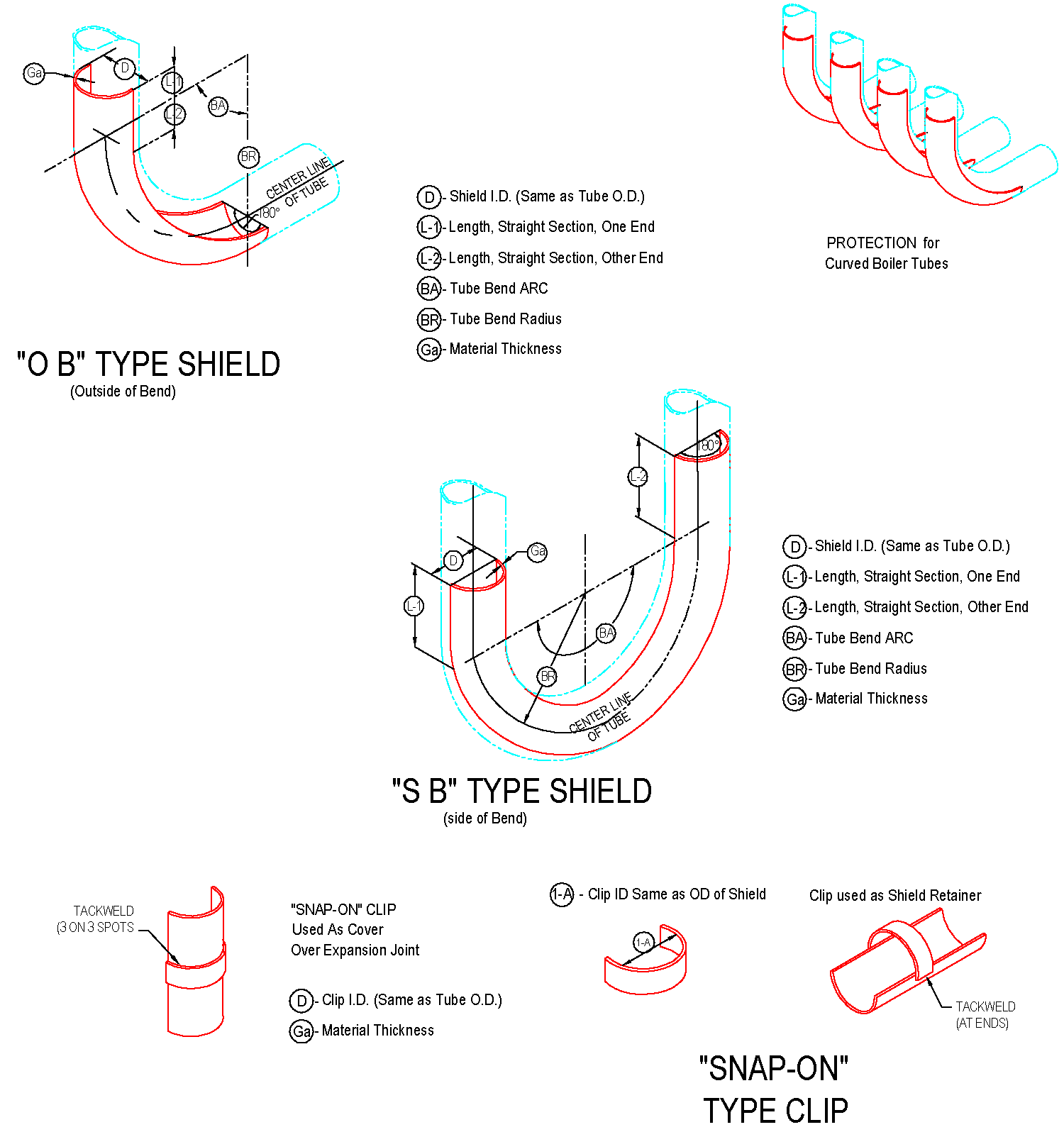
The length of the straight anti-wear shields ranges from 20mm to 3000mm, and the general length of 1000-2000mm is commonly used. The anti-wear shields with bends generally requires a processing drawing and the following parameters should be on the drawing: outer diameter of the pipe used, bending of the pipe Radius R (to the center of the pipe), the degree of bending angle, and the length of the straight sections on both sides of the arc segment of the wear-resistant shields.
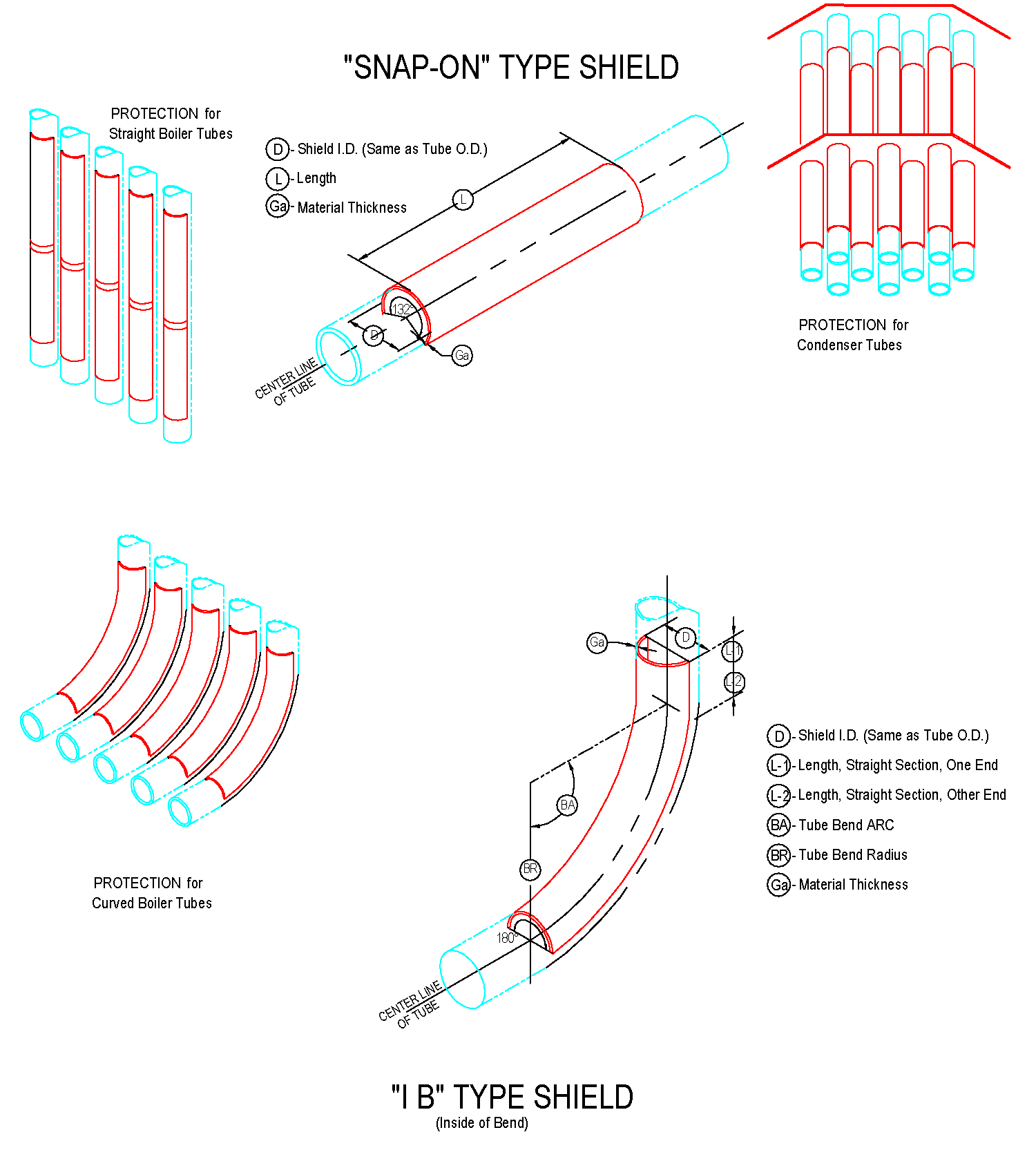
The most basic parameter of boiler tubes shields is the outer diameter of the tube used (that is, the inner diameter of boiler tubes erosion shields). The main specifications of the tube are: 32, 38, 42, 44.5, 48, 51, 57, 60, 63.5 , 76, 89mm, etc . the inner diameter of the boiler tubes erosion shields is usually 1-3mm larger than the outer diameter of the tube used, depending on the actual requirements.
Generally, boiler tubes erosion shields are also installed to prevent further wear of the tubes and cause serious consequences such as boiler explosion.
The main role is to protect the heating surface of the boiler pipes, reduce pipeline wear, and increase the heating surface of the pipes.
